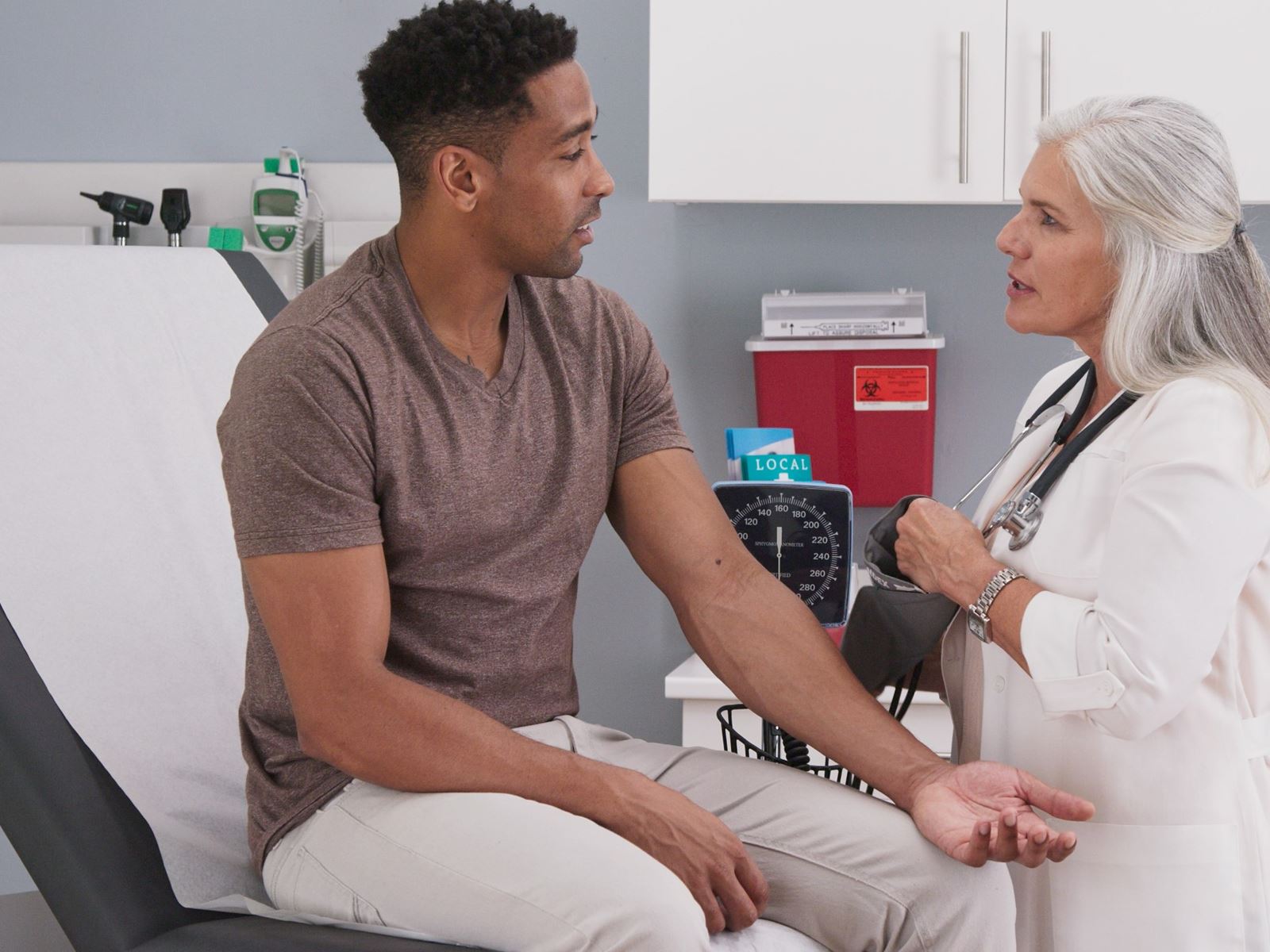
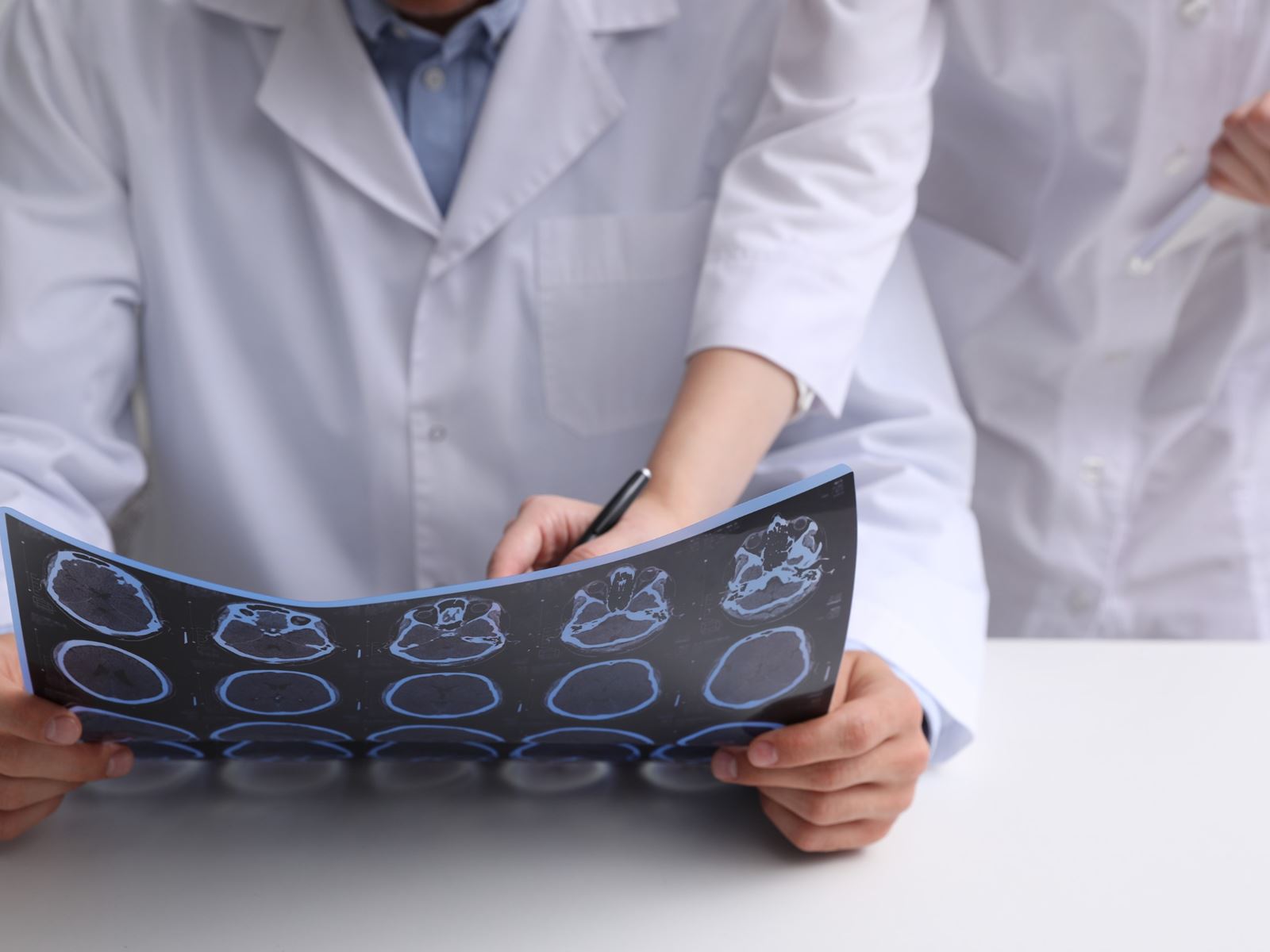
Clinical Signs and Symptoms
Relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis follows a pattern in which one develops signs and symptoms of a neurological disturbance in the brain or spinal cord. The relapses progress over a few days, stabilize, and typically resolve after a few weeks. Optic neuritis is a common presenting symptom of multiple sclerosis. It causes pain with eye movement and decreased vision in the eye affected. Other symptoms during a relapse include double vision, numbness, tingling, slurred speech, limb weakness, clumsiness, imbalance, bowel, and bladder symptoms. These symptoms can completely resolve or one may remain with a partial deficit. Additional symptoms common to patients with multiple sclerosis include fatigue, heat intolerance, depression, and spasticity. If the symptoms progress between attacks then the disease is categorized to be in the secondary progressive stage. Patients with primary progressive multiple sclerosis develop a gradual accumulation of disability without relapses.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of multiple sclerosis is based on clinical attacks and MRI evidence of typical lesions. The use of MRI for multiple sclerosis has evolved as a valuable tool used to establish an early diagnosis and monitor disease progression. The MRI pictures depicted indicate areas of demyelination or plaques in the cervical spinal cord (figure 7) and in the brain (figure 8). Infusion with gadolinium may reveal enhancement and would be consideredd "active" lesions (figure 9). Additional testing may be required to establish the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Lumbar punctures are performed to sample the cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) to examine for evidence of inflammation. We are looking for the presence of oligoclonal bands (figure 10) or an elevation of the IgG index. Visual evoked potentials may be obtained to evaluate for evidence of previous damage to the optic nerve from a demyelinating event (figure 11). At times, brainstem auditory evoked potentials or somatosensory evoked potential are obtained.
Symptoms & Treatment
The following symptoms are very common among MS patients.
Fatigue in MS may be due to certain lesions affecting specific parts of the brain. It is the most common symptom of MS. As many as 75% to 95% of all people with MS have fatigue; 50% to 60% say that it’s one of their worst problems. No one quite understands what causes MS related fatigue, but we do know some things that can help.
MS related fatigue may have some unique characteristics that make it different from the normal feeling of being tired. MS patients may notice some of the following features associated with their fatigue:
- Generally occurs on a daily basis
- May occur early in the morning, even after a restful night's sleep
- Tends to worsen as the day progresses
- Tends to be aggravated by heat and humidity
- Comes on easily and suddenly
- Is generally more severe than normal fatigue
- Is more likely to interfere with daily responsibilities
Some Strategies for Dealing with Fatigue Include:
- Physical therapy: May learn energy-saving ways of walking (with or without assistive devices) and performing other daily tasks, and to develop a regular exercise program.
- Sleep regulation: May involve treating other MS symptoms that interfere with sleep (e.g., spasticity, urinary problems) and using sleep medications on a short-term basis.
- Psychological interventions: Stress management, relaxation training or Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
- Heat management: Find ways to avoid overheating and how to cool down quickly.
- Rest and Conserve: Take short breaks throughout the day. Rest before you get tired! Take advantage of using that handicapped permit and park close to the building. That does not mean you're giving in; it means you're being smart.
- Exercise: This seems counterintuitive, but exercising boosts energy by strengthening easily tired muscles
- Ask for help: It's ok to delegate some work to others. Be specific about what you need.
Medications that can help:
| Drug Name | Dose in MS | Drug profile |
|---|---|---|
| Amantadine | 100 mg morning and early afternoon | Antiviral agent typically used in influenza or Parkinson's disease treatment—has also shown fatigue relief for some with MS |
| Modafinil (Provigil) | 100-200 mg a day | Wakefulness-promoting agent for treating narcolepsy that a study has shown reduces self-reported fatigue for some people with MS |
| Methylphenidate (Ritalin), Amphetamine & Dextroamphetamine (Adderall) | 10–20 mg early morning and at noon | A central nervous system stimulant indicated for treatment of attention deficit disorders but also helpful for MS fatigue in some people |
Source: National MS Society Medical Advisory Board
Many patients with MS may experience problems with their bowels.
Normal bowel functioning can range from 3 bowel movements a day to 3 a week. While you may have heard that "one movement a day," is the norm, such frequency is not necessary. The medical definition of "infrequent" bowel movements is "less often than once every 3 days."
Constipation is the most common bowel complaint in MS.
In addition to the disease itself, other contributing factors to constipation in MS patients may include, inactivity; difficulty in walking and fatigue which can slow movement of waste material through the colon. Medications such as calcium supplements or antacids containing aluminum or calcium can also contribute to constipation. Additionally, other drugs such as some antidepressants, diuretics, opiates, and antipsychotic drugs may also lead to constipation. Finally, some people with MS try to solve bladder problems by reducing their fluid intake. However, restricting fluids can make constipation worse.
Besides the obvious discomfort of constipation, complications can develop. Stool that builds up in the rectum can put pressure on parts of the urinary system, increasing some bladder problems.
Forming Good Bowel Habits
- Drink enough fluids: Each day, drink 8–12 cups of liquid whether you are thirsty or not. Water, juices, and other beverages all count
- Put fiber into your diet: Fiber is plant material that holds water and is resistant to digestion. It is found in whole-grain breads and cereals as well as in raw fruits and vegetables. Fiber helps keep the stool moving by adding bulk and by softening the stool with water
- Get your regular physical activity: Walking, swimming, and even chair exercises help
Medications/tools that can help
- Stool softeners: Examples are Colace® and Surfak. These medications often contain docusate, a surfactant that helps to "wet" and soften the stool.
- Bulk-forming supplements: Natural fiber supplements include Metamucil®, Benefiber, FiberCon, Citrucel®, or Fiberall. These supplements are often taken daily with 1-2 glasses of water. They are generally safe to take for long periods.
- Saline laxatives: Milk of Magnesia, Epsom salts, and sorbitol are all osmotic agents. They promote secretion of water into the colon. They are reasonably safe, but should not be taken on a long-term basis.
- Stimulant laxatives: Some brands include Ex-Lax, Senokot, Correctol, Dulcolax, These medications provide a chemical irritant to the bowel, which stimulates the passage of stool. Peri-Colace includes senna plus a stool softener.
Note: Don't use stimulant laxatives daily or regularly. This type of laxative may weaken the body's natural ability to defecate and cause laxative dependency. One more caveat: the stimulant laxatives may cause cramping and diarrhea. - Suppositories: If oral laxatives fail, you may be told to try a glycerin suppository half an hour before attempting a bowel movement. Dulcolax® suppositories stimulate a strong, wave-like movement of rectal muscles.
- Enemas: Enemas should be used sparingly, but they may be recommended as part of a therapy that includes stool softeners, bulk supplements, and mild oral laxatives.
Bowel Incontinence:
Accidents can happen. This can be embarrassing and stressful. Try to keep a regular bowel regimen to prevent an uncomfortable situation.
If you know you might be in a situation where you'll be at risk for an accident, you can try to induce a bowel movement on your own beforehand with the help of enemas or suppositories.
Bladder problems are very common among MS patients. In fact, 70 – 80% of patients with MS may experience problems with bladder function.
Symptoms of Neurogenic Bladder include:
- Frequency and/or urgency of urination
- Hesitancy in starting urination
- Incontinence (the inability to hold in urine)
- Frequent nighttime urination (nocturia)
- Inability to empty the bladder completely and/or double voiding
Other causes of bladder dysfunction:
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- Pelvic floor relaxation in women
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) in men
What can I do on my own to help with my bladder problems?
The Do's and Don'ts of Bladder Dysfunction in MS
DO:
- Do drink at least 48-64oz of fluid a day (1.4-2 liters) to keep well hydrated. Water is always best.
- Do limit the amount of caffeinated beverages you consume. It's ok to have a cup of coffee or tea, but remember, caffeine can cause increased bladder activity and can exacerbate symptoms, including urgency and frequency, as well as increased incontinence.
- Do limit alcohol intake. Yes, alcohol is also a bladder irritant.
- Do limit carbonated beverages. The fizz in carbonated beverages can potentially aggravate bladder symptoms.
- Do try to limit fluid intake past 7:00pm to avoid frequent trips to the bathroom overnight.
DON'T:
- Don't Smoke! Smoking irritates the bladder muscle, and spasms caused by smoker’s cough can result in further urine leakage.
- Don't try to self-treat your bladder problems by drinking less fluid! Don’t let yourself become dehydrated. This can lead to constipation and sometimes urinary tract infections.
- Don't wait for the urge! Drink 6-8oz of fluid at regular intervals and then urinate on a regular schedule. It usually takes about 1.5 hours for fluid that you drank to get to the bladder, so try to void every 1.5-2 hours.
What are the potential pharmacologic treatments for bladder dysfunction?
Commonly used medications for urgency, frequency and incontinence include a class of drugs called anticholinergic/antimuscarinic agents.
Examples of these medications include:
- Oxybutynin (Ditropan/XL®)
- Oxybutynin transdermal
- Tolterodine (Detrol®/LA)
- Solifenacin succinate (VESIcare®)
- Darifenacin (Enablex®)
- Fesoterodine fumarate (Toviaz®)
Other medications used for bladder problems include:
- Mirabegron (Myrbetriq®) – This drug works by a different mechanism of action than the medications listed above. It is a beta-3 adrenergic receptor agonist.
- DDAVP (desmopressin)
- Flomax® (tamsulosin)
- Hytrin® (terazosin)
- Minipress® (prazosin)
Other Treatments:
- Botulinum Toxin (Botox®)
Botox can be injected into the bladder wall to help with bladder spasticity and relax bladder muscles. Botox has been used to treat urinary incontinence for many years. It acts to decrease the muscular contractions of the bladder and improved the bladder carrying capacity. This is often a short procedure that takes place in a urology clinic or operating room. The effect from the injections can last up to about 6 months. - Intermittent self-catheterization or indwelling catheter.
This can be particularly helpful for patients that have difficulty emptying their bladder.
Referral to Urology:
- You may be referred to a urologist for urodynamic testing. Urodynamics is a study that assesses how well the bladder and urethra are storing and releasing urine.
- A urologist is the person who administers Botox injections.
Depression is very common among MS patients. Depression in MS may be due to the disease itself which may affect the signals in the brain that affect mood. Depression can also a side effects of some the drugs that treat MS, such as steroids or interferon.
More than half of all people with MS are likely to experience a depressive episode over their lifetime compared to 20% of the general population.
Anxiety, difficulty controlling emotions (mood swings), pseudobulbar affect (inappropriate or uncontrollable laughing and weeping), and euphoria also occur in MS.
It is not uncommon for family members to also become depressed and anxious as they struggle to cope with the challenges of the illness affecting their loved one. MS affects the whole family.
What are the symptoms of Depression?
Depression is characterized by:
- Depressed mood or loss of interest or pleasure
- Feelings of hopelessness or pessimism
- Feelings of guilt, worthlessness, or helplessness
- Sleep disturbances: trouble falling or staying asleep, early morning awakening, sleeping too much (this can be confused with sleep disturbances caused by MS)
- Diminished appetite with weight loss or increased appetite with weight gain
- Decreased energy, increased fatigue, and feeling "slowed down" (this can be easily confused with MS-related fatigue)
- Restlessness or agitation and/or irritability
- Diminished ability to think, concentrate, or make decisions (this can be easily confused with MS-related cognitive impairment)
- Thoughts of suicide or death or a suicide plan or attempt
When are MS patients most vulnerable to depression?
People with MS can become depressed at any time, but certain times and experiences are associated with greater risk:
- The time at diagnosis
- During an exacerbation or relapse
- Noticing increasing disability
- A transition point to greater dependence – i.e. the need for a cane, transitioning to a wheelchair
- Any major life change or loss, such as retiring for disability-related reasons
What are some of the medications for depression?
- Prozac (Fluoxetine) 10mg-40mg daily
Side Effects: Weight gain, sexual side effects, agitation, insomnia - Sertraline (Zoloft) 50mg-200mg daily
Side Effects: Sexual side effects, loss of appetite, GI side effects, agitation, insomnia - Escitalopram citrate (Lexapro) 10mg-20mg daily
Side Effects: Sexual side effects, nausea, diarrhea, agitation, insomnia - Citalopram (Celexa) 20mg-60mg daily
Side Effects: syncope, lightheadedness, tremor, hallucinations, sexual side effects - Venlafaxine (Effexor) 37.5mg-225mg long-acting forms given once daily
Side Effects: tachycardia, hypotension, sexual side effects, nausea, weight loss - Bupropion (Wellbutrin) 100mg-300mg in divided doses
Side Effects: lowers seizure threshold, nausea, constipation, headache, insomnia, rare Stevens-Johnson syndrome
What you can do:
- Talk to your neurologist or primary care doctor about finding a mental health provider who can help you.
- Psychiatrists, psychologists, social workers, and psychiatric nurses all work with patients and families in psychotherapy.
- Chapters of the National Multiple Sclerosis Society (1-800-344-4867) can provide names of mental health professionals in the community who are experienced with treating the emotional disturbances associated with MS.
- The chapters also offer educational programs, support groups, and other resources to support patients' coping efforts and help them deal with MS-related emotional changes.
Recommended Books:
- Feinstein A. The Clinical Neuropsychiatry of Multiple Sclerosis (2nd ed.). New York: Cambridge University Press, 2007.
- Kalb R (ed.). Multiple Sclerosis: The Questions You Have; The Answers You Need (4th ed.). New York: Demos Medical Publishing, 2008.
- Kalb R (ed.). Multiple Sclerosis: A Guide for Families (3rd ed.). New York: Demos Medical Publishing, 2006.
- Kalb R, Holland N, Giesser B. Multiple Sclerosis for Dummies. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley Publishing, 2007
- Minden S. Pseudobulbar Affect (Uncontrollable Laughing and/or Crying) Visit Site Here
- Pitzele S. We Are Not Alone: Learning to Live with Chronic Illness. New York: Workman Press, 1986.
Treatment Overview
At the Brigham MS center we share a vision to treat MS patients early in order to secure better long term outcomes for our patients. We recognize that patients are individuals and will require that medicines are tailored to their needs. We carefully monitor our patients and will reassess our treatment approach at the first sign of any disease activity. We also believe that effective symptom management is at the core of successful MS treatment.
Over the past two decades, there has been considerable progress in the treatment of multiple sclerosis. There are now several therapeutic options available to patients. Your doctor will discuss these treatment options in detail and recommend treatments that are appropriate for your care. The following medications are available for patients:
Injectable Disease Modifying Therapies
- Betaseron (interferon beta 1b)
- subcutaneous injection taken every other day.
- Avonex (interferon beta 1a)
- intra muscular injection taken once weekly.
- Rebif (interferon beta 1a)
- subcutaneous injection taken 3 times per week.
- Copaxone/ Glatopa(glatiramer acetate)
- subcutaneous injection taken 3 times a week or daily.
Oral Disease Modifying Therapies
- Gilenya (fingolimod)
- pill taken once a day
- Tecfidera (dimethyl fumarate)
- pill taken twice a day
- Aubagio (teriflunomide)
- pill taken once a day
- Mayzent (siponimod)
- pill taken once daily
- Mavenclad (cladribine)
- pills taken as two treatment courses over 2 years. Each treatment course consists of 2 treatment weeks, one month apart
Infusion Disease Modifying Therapies
- Tysabri (natalizumab)
- Once a month infusion
- Ocrevus (ocrelizumab)
- Once every 6 months
- Lemtrada (alemtuzumab)
- 5 infusion days – one year later 3 infusion days – additional infusions as needed
For Management of Acute Relapses
Steroids
- Intravenous methylprednisolone (Solumedrol) is used to treat relapses or exacerbations. It is given for 3 to 7 days with the premise that treatment decreases the duration and severity of the present attack.
- Intravenous methylprednisolone may be given on a once monthly basis as an addition to a baseline medication.
Disease Modifying Treatments
Brand Name
"Solumedrol®"
What it is
An injectable medication that is a potent steroid with anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressant properties.
What it does
- Decreases active inflammation
- Short courses with high doses may stabilize active disease during a relapse
- Certain patients may receive regular doses of steroids in an attempt to alter the progression of the disease.
How it works
It reduces the immune system's ability to seek out and attack the nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord.
How it's given
- Intravenously – in the multiple sclerosis center infusion room
- Infused over 90 minutes
- Dose:
- 500-1000 mg
- May be given once daily for 3 – 7 days for a relapse
- May be given once a month for long term therapy
Possible Side Effects
- Short-term
- Report any pain or discomfort near the IV site to your nurse
- Headache, facial flushing (reddening)
- Taste disturbances (metallic)
- Increased blood sugar
- Increased risk of infection
- Nausea, vomiting, stomach pain
- Increased blood pressure
- Imbalance or increase of water and sodium retention
- Leg cramps
- Personality changes, difficulty sleeping, depression, irritability
- Long-term
- Increased risk of infection
- Impaired wound healing
- Hair loss, thinning of the skin
- Ulcers of stomach, mouth
- Weight gain
- Weakened bones (osteoporosis)
- Cataracts, glaucoma
- Rare hip disease called avascular necrosis
Tips
- For difficulty sleeping, some over-the-counter medications such as Benadryl® (diphenhydramine) may help. Tylenol PM® contains the active ingredient in Tylenol® (acetaminophen) plus diphenhydramine and is ok to take but is no better than plain Benadryl® (diphenhydramine) for sleep unless you have pain that you need the acetaminophen for also.
- Check with your pharmacist or physician before taking over-the-counter medications.
- Having a piece of hard candy may help mask the metallic taste.
- Patients with diabetes should check their blood sugars more frequently during the first 24-48 hours after steroid treatment.
- Your physician may instruct you to take an antacid such as Zantac® or Pepcid® while taking methylprednisolone.
- Drink orange juice or eat bananas on the days that you receive methylprednisolone. This will help to replenish your potassium stores and may help to prevent leg cramps.
- Taking this medication may make you more susceptible to infections so you should avoid contact with sick people and wash your hands often.
- Most patients on long-term steroid treatments should take a calcium and vitamin D supplement to prevent osteoporosis.
- Talk to your health care provider before receiving any vaccines.
- Some vaccines you should avoid while others may not work while on this medication.
When to contact your healthcare provider
If you are experiencing:
- Chest tightness, trouble breathing, wheezing
- Rash, hives, extreme itchiness
- Swelling of the face or lips and swelling or tingling of the tongue and throat
- High fever, severe sore throat or any other signs of infection
- Fast heartbeat (palpitations), sweating, confusion
- Sudden pain or swelling in the legs, ankles, feet or hands
- Extreme headache, eye pain or trouble seeing
- Abnormal muscle pain or weakness
- If your stool is very black or you see blood in your stool
- Although methylprednisolone may be given to you if you are pregnant or breastfeeding an infant, contact your physician if you are or if you think you may be or if you would like to become pregnant or breastfeed an infant.
Patient Information For:
Interferon beta-1a
Brand Name:
Avonex® and Rebif®
What it is:
Avonex® and Rebif® are self-injectable medications, both containing the active ingredient, interferon beta-1a, but are clinically different formulations and should not be interchanged. These are also similar to Betaseron® (interferon beta-1b) but should not be interchanged. These medications are sometimes referred to as "injectables" or "A, B, C therapy."
What it does
- Reduces the number of relapses
- Slows the accumulation of physical disability
How it works
Interferon beta-1a is a naturally occurring protein that is usually produced in response to certain infections. Its role, though, is thought to be more of a regulatory one, keeping the immune system in check. It alters the way in which certain white blood cells, T-cells, respond to "foreign" material.
How it's given
Avonex®
- Avonex® prefilled syringes are available in cartons of 4 single-use prefilled syringes so it does not have to be prepared or drawn up ahead of time.
- Each syringe should only be used once and then discarded appropriately.
- Avonex® is also available in vials containing powder that must be mixed prior to injection. Although, not commonly used, you will be instructed on this process if you are given these and provided with all supplies necessary.
- Dose: 30 mcg once a week
- Avonex® is injected intramuscularly (in the muscle)
- A nurse or your physician should show you how to inject this medication.
- Your first, self-administered dose should be done under the direct supervision of an appropriately qualified health care practitioner.
- You should review the information provided for you when you begin Avonex® therapy and with each refill.
- After the injection, dispose the used syringe into a hard-welled container.
Rebif®
- Rebif® is available in single-use prefilled syringes so it does not have to be prepared or drawn up ahead of time.
- Each syringe should only be used once and then discarded appropriately. You may only use part of a syringe when starting therapy (see dosing below), but you should still discard unused portions.
- Dose: increased slowly to 22 mcg or 44 mcg three times weekly
- Dose is slowly increased to reduce side effects
| Week | Percentage of final dose | For final target dose of Rebif® | For final target dose of Rebif® |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weeks 1-2 | 20% | 4.4 mcg | 8.8 mcg |
| Weeks 3-4 | 50% | 11 mcg | 22 mcg |
| Weeks 5+ | 100% | 22 mcg | 44 mcg |
- Rebif® is injected subcutaneously (under the skin)
- A nurse or your physician should show you how to inject this medication.
- Your first, self-administered dose should be done under the direct supervision of an appropriately qualified health care practitioner.
- You should review the information provided for you when you begin Rebif® therapy and with each refill.
- After the injection, dispose the syringe into a hard-welled container.
Storage
- Prefilled Avonex® and Rebif® syringes should be kept in their original blister package and in the original carton, under refrigeration (36-46°F or 2-8°C).
- You may store Avonex® in its original blister packages and in the original carton at room temperature (59-86°F or 15-30°C), for up to 7 days.
- You may store Rebif® in its original blister packages and in the original carton at room temperature (59-86°F or 15-30°C), for up to 30 days.
- Avonex® and Rebif® should NEVER be stored in the freezer.
- Avonex® and Rebif® are sensitive to light, meaning that it will degrade with excessive exposure, so you should always protect the syringes from direct light until its time to inject it.
- The solution should be clear but may appear slightly yellow. Do not use a syringe if the solution appears cloudy or you see that it contains particles. Return it to your pharmacy.
General Injection Information
- If storing Avonex® or Rebif® under refrigeration, remove the syringe from the refrigerator 30 minutes before you inject, allowing it to warm to room temperature.
- Always wash and dry your hands before and after injecting.
- Chose a site that is at least 2 inches from the last site of injection.
- Never inject into the same area on your body more than once a week.
- Acceptable sites for Rebif®: stomach, arm, thigh, hip
- Acceptable sites for Avonex®: upper arm or thigh muscle
- After the injection, dispose the used syringe into a hard-welled container.
Possible Side Effects
- Flu-like symptoms: fever, chills, fatigue, muscle aches
- Dizziness, headache
- Pain, redness, swelling, and irritation at the injection site
- Depression, mood changes, anxiety
- Liver damage: pain in the upper, right area of your torso, yellow coloring of skin and eyes
- Thyroid changes: feeling hot or cold all of the time or weight change without a change in your diet or activity are common symptoms
- Blood disorders such as anemia or easy bruising or abnormal bleeding
Tips
- Do not stop taking this medication or change the dose or dosing schedule without speaking with your physician.
- Always call your refills in to your pharmacy before you are out of medication to avoid any disruption in therapy.
- This medication should not be used if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
- Always use birth control to prevent pregnancy while on this medication and speak with your physician or pharmacist before breastfeeding while on this medication.
- For information about birth control options, speak with your physician or pharmacist.
- If you are experiencing flu-like symptoms (fever, chills, fatigue, muscle aches) you can try taking some over-the-counter medications to prevent this. Check with your pharmacist or physician before taking these: Tylenol® (acetaminophen) or Advil® (ibuprofen)
- Taking this medication may make you more susceptible to infections so you should avoid contact with sick people and wash your hands often.
- If you miss a dose of your medication, take it as soon as you remember:
- Avonex®: you can resume your regular schedule but don’t take doses within 2 days of each other
- Rebif®: you should skip the next day if you are scheduled to take it. It should not be taken on 2 consecutive days. You can resume your normal schedule the following week.
- Always have your blood checked when scheduled by your physician.
- Talk to your health care provider before receiving any vaccines.
- Some vaccines you should avoid while others may not work while on this medication.
When to contact your healthcare provider
If you are experiencing:
- Chest tightness, trouble breathing, wheezing
- Rash, hives or severe itching
- Swelling of face, lips, tongue or throat
- High fever, severe sore throat or any other signs of infection
- Fast heartbeat, sweating, confusion
- Signs and symptoms of depression or any thoughts of suicide
- If you were told you have liver damage or you think you may be having symptoms of liver toxicity: pain in the upper, right area of your torso, yellow coloring of skin and eyes (jaundice) or itching.
- Other non-specific symptoms include: fatigue, weakness, abdominal pain, loss of appetite
- You should not become pregnant or breastfeed an infant while using this medication.
- Contact your physician if you are or if you think you may be or if you would like to become pregnant or breastfeed an infant.
Patient Information For
Interferon beta-1b
Brand Name
Betaseron®
What it is
"Betaseron®" is a self-injectable medication and was the first disease modifying medication approved for treating multiple sclerosis. The active ingredient, interferon beta-1b, is similar to the active ingredient in Avonex® and Rebif®, interferon beta-1a, but is different and should not be interchanged. Betaseron® is sometimes referred to as one of the "injectables" or "A, B, C therapy."
What it does
- Reduces the number of relapses
- Slows the accumulation of physical disability
How it works
Interferon beta-1b is a naturally occurring protein that is usually produced in response to certain infections. Its role, though, is thought to be more of a regulatory one, keeping the immune system in check. It alters the way in which certain white blood cells, T-cells, respond to "foreign" material.
How it's given
Betaseron®
- Betaseron® is available in a vial containing powder and comes with a vial of sodium chloride solution (the diluent) so it must be prepared and drawn up before injecting.
- You will be instructed on this procedure by your physician or a nurse when starting therapy and will be given prescriptions for supplies when necessary and instruction on what additional materials you will need for this procedure.
- Dose: increased slowly to 0.25 mg every other day
- Approximately 48 hrs apart so the same time every day is best.
- Dose is slowly increased to reduce side effects
| Week | Percentage of final dose | Dose of Betaseron® | Volume |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weeks 1-2 | 25% | 0.0625 mg | 0.25 ml |
| Weeks 3-4 | 50% | 0.125 mg | 0.5 ml |
| Weeks 5-6 | 75% | 0.1875 mg | 0.75 ml |
| Weeks 7+ | 100% | 0.25 mg | 1 ml |
- Betaseron® is injected subcutaneously (under the skin)
- A nurse or your physician should show you how to inject this medication.
- Your first, self-administered dose should be done under the direct supervision of an appropriately qualified health care practitioner.
- You should review the information provided for you when you begin Betaseron® therapy and with each refill.
- After the injection, dispose the syringe into a hard-welled container.
Storage
- Betaseron® powder and diluent should be stored in the original container and at room temperature, preferably 77°F (25C°), definitely within 59-86°F or 15-30°C.
- After mixing, the solution should be used right away.
- If you do not use it right away, it should be stored under refrigeration (36-46°F or 2-8°C) and must be used within 3 hours of mixing.
- Always discard unused portions even if you are only using part of a vial.
- Betaseron® should NEVER be stored in the freezer.
- Betaseron® is sensitive to light, meaning that it will degrade with excessive exposure, so you should always protect the powder and diluent or prepared solution from direct light until its time to mix or inject it.
General Injection Information
- Always wash and dry your hands before and after injecting.
- Never inject into the same area on your body more than once a week.
- Acceptable sites: stomach, arm, thigh, hip
- Chose a site that is at least 2 inches from the last site of injection.
Possible Side Effects
- Flu-like symptoms: fever, chills, fatigue, muscle aches
- Dizziness, headache
- Pain, redness, swelling, and irritation at the injection site
- Depression, mood changes, anxiety
- Liver damage: pain in the upper, right area of your torso, yellow coloring of skin and eyes
- Thyroid changes: feeling hot or cold all of the time or weight change without a change in your diet or activity are common symptoms
- Blood disorders such as anemia or easy bruising or abnormal bleeding
Tips
- Do not stop taking this medication or change the dose or dosing schedule without speaking with your physician.
- Always call your refills in to your pharmacy before you are out of medication to avoid any disruption in therapy.
- This medication should not be used if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
- Always use birth control to prevent pregnancy while on this medication and speak with your physician or pharmacist before breastfeeding while on this medication.
- For information about birth control options, speak with your physician or pharmacist.
- If you are experiencing flu-like symptoms (fever, chills, fatigue, muscle aches) you can try taking some over-the-counter medications to prevent this. Check with your pharmacist or physician before taking these: Tylenol® (acetaminophen) or Advil® (ibuprofen)
- Taking this medication may make you more susceptible to infections so you should avoid contact with sick people and wash your hands often.
- If you miss a dose of your medication, take it as soon as you remember:
- Betaseron®: you should skip the next day if you are scheduled to take it. It should not be taken on 2 consecutive days. You can resume your normal schedule the following week.
- Always have your blood checked when scheduled by your physician.
- Talk to your health care provider before receiving any vaccines.
- Some vaccines you should avoid while others may not work while on this medication.
When to contact your healthcare provider
If you are experiencing:
- Chest tightness, trouble breathing, wheezing
- Rash, hives or severe itching
- Swelling of face, lips, tongue or throat
- High fever, severe sore throat or any other signs of infection
- Fast heartbeat, sweating, confusion
- Signs and symptoms of depression or any thoughts of suicide
- If you were told you have liver damage or you think you may be having symptoms of liver toxicity: pain in the upper, right area of your torso, yellow coloring of skin and eyes (jaundice) or itching.
- Other non-specific symptoms include: fatigue, weakness, abdominal pain, loss of appetite
- You should not become pregnant or breastfeed an infant while using this medication.
- Contact your physician if you are or if you think you may be or if you would like to become pregnant or breastfeed an infant.
Brand Name
"Copaxone®"
What it is
Glatiramer acetate is a self-injectable medication consisting of 4 naturally occurring proteins, specifically: L-glutamic acid, L-alanine, L-tyrosine, and L-lysine. It was chemically designed to mimic myelin basic protein, which is involved with the activation of the immune system to attack the myelin that covers the neurons in the central nervous system. Copaxone® is sometimes referred to as one of the "injectables" or "A, B, C therapy."
What it does
In studies, glatiramer has been shown to decrease relapse rates in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Some data suggest that it may slow the progression of multiple sclerosis, and offer a neuroprotective effect.
How it works
Although the mechanism is not completely understood, glatiramer is thought to work by modifying the way in which certain white blood cells, including T-helper cells and T-suppressor cells, react to myelin, which is one major target in multiple sclerosis. When administered to multiple sclerosis patients, glatiramer is presented to these T-cells, which induces a protective state that is normally present in non-multiple sclerosis patients.
How it's given
- Copaxone® is available in cartons of 30 single-use prefilled syringes so it does not have to be prepared or drawn up ahead of time.
- Each syringe should only be used once and then discarded appropriately.
- Dose: 20 mg every day
- Copaxone® is injected subcutaneously (under the skin)
- A nurse or your physician should show you how to inject this medication.
- Your first, self-administered dose should be done under the direct supervision of an appropriately qualified health care practitioner.
- You should review the Copaxone® injection patient information leaflet, which will be presented to you before you begin Copaxone® therapy and with each refill.
Storage
- Prefilled Copaxone® syringes should be kept in their original blister package and in the original carton, under refrigeration (36-46°F or 2-8°C).
- You may store Copaxone® in its original blister packages and in the original carton at room temperature (59-86°F or 15-30°C), for up to 30 days.
- Do not store Copaxone® at room temperature for longer than 30 days and NEVER in the freezer.
- Copaxone® is sensitive to light, meaning that it will degrade with excessive exposure, so you should always protect the syringes from direct light until its time to inject it.
- Do not use a syringe if the solution appears cloudy or you see that it contains particles. Return it to your pharmacy.
General Injection Information
- Refer to the COPAXONE® INJECTION PATIENT INFORMATION Leaflet for more information. Shared Solutions™ at (800)-887-8100 has several educational materials that may also be helpful.
- If storing Copaxone® under refrigeration, remove the syringe from the refrigerator 20 minutes before you inject, allowing it to warm to room temperature.
- Always wash and dry your hands before and after injecting.
- Never inject into the same area on your body more than once a week.
- Acceptable sites: stomach, right and left arm, right and left thigh, right and left hip.
- Chose a site that is at least 2 inches from the last site of injection.
- Do not rub the injection site on the same day as you have injected yourself.
- After the injection, dispose the used syringe into a hard-welled container.
Possible Side Effects
- Redness, pain, swelling, itching, or a lump at the injection site
- A permanent depression under the skin at the injection site may occur
- Swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck, armpits or groin areas
- Fluid retention, facial swelling, weight gain
- Nausea, vomiting, shortness of breath, sweating
- Tremor, muscle pain, neck pain, weakness
- Anxiety, hand shakes
- Low blood pressure – dizziness, heart beating fast when standup
- Immediate Post-Injection Reaction (IPIR)
- In approximately 10% of patients given Copaxone® in trials, a post-injection reaction occurred, usually within minutes after injecting, and included flushing (feeling warmth and/or appearing red), chest tightness or pain with palpitations, anxiety and trouble breathing. Referred to as the Immediate Post-Injection Reaction (IPIR), symptoms lasted for only a few minutes and resolved without any treatment required. Generally, this reaction happens several months after starting the medication but may occur anytime. Most patients only have it once but it can happen several times. If you experience this after being on Copaxone® for a while, it is important to try to relax, keep your head upright, and breathe slowly. If this reaction does not go away on its own or if you have symptoms of tongue or face swelling, or experience extreme trouble breathing, seek immediate medical attention. Either way, you should contact your physician describing the experience, and do not give yourself anymore injections until your physician tells you to begin again.
- Chest pain
- In trials, several patients experienced chest pain as a lone symptom that was not related to any other symptom as described above with the IPIR and did not necessarily occur immediately after injecting. It lasted only a few minutes and most episodes occurred after at least one month of therapy.
- Increased risk of infection (theoretical, as this has not been observed or evaluated)
Tips
- Do not stop taking this medication or change the dose or dosing schedule without speaking with your physician.
- Always call your refills in to your pharmacy well before you are out of medication to avoid any disruption in therapy. Most mail order pharmacies require at least a week to confirm your prescription and ship the medication.
- Taking this medication may make you more susceptible to infections so you should avoid contact with sick people and wash your hands often.
- You should not use this medication if you are allergic to glatiramer or mannitol.
- This medication should not be used if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
- Always use birth control to prevent pregnancy while on this medication and speak with your physician or pharmacist before breastfeeding while on this medication.
- For information about birth control options, speak with your physician or pharmacist.
When to contact your healthcare provider
- If you think you have had an Immediate Post-Injection Reaction (IPIR) as described above. Do not give yourself any more injections until your physician tells you to begin again.
- Severe injection site pain or severe pain anywhere
- Painful lumps in the neck, groin or armpits
- Chest tightness, trouble breathing, wheezing
- Rash, hives or severe itching
- Swelling of face, lips, tongue or throat
- High fever, severe sore throat or any other signs of infection
- Fast heartbeat, sweating, confusion
- You should not become pregnant or breastfeed an infant while using this medication without discussing it with your physician first.
- Contact your physician if you are or if you think you may be or if you would like to become pregnant or breastfeed an infant.
Brand Name
Gammagard Liquid, Gammagard S/D, Gammunex (several other brands exist)
What it it
IgG is an injectable medication, which contains many different antibodies that are normally present in the body. It is collected from large pools of human plasma and is screened and treated extremely well for potentially infectious agents including hepatitis B and C, HIV and others.
What it does
In some studies IgG has been shown to decrease the frequency and severity of relapses in patients with relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis. Studies also suggest that IgG given to women with multiple sclerosis after giving birth, decreases the relapse rate during the following 6 months, which is typically a period associated with an abnormally elevated rate.
How it works
- Many mechanisms have been described:
- One thought is that it binds to white blood cells and decreases their attraction to and destruction of the nerve cells in the brain.
- It may also work by overloading your own immune system, which tricks it into reacting less to your own nerve cells.
How it's given
- Intravenously – in the multiple sclerosis center infusion room
- Infused over several hours depending on your dose and prior use
- Dose
- Based on weight: 1 gm per kilogram
- Usually given once monthly
- Duration
- Infusions can take up to 6 hours. You should schedule your infusion to start first thing in the morning.
Possible Side Effects
- Short-term
- Report any pain or discomfort near the IV site to your nurse
- Headache, dizziness, nausea, vomiting
- Fever, chills, shaking
- Long-term
- Back pain
- Increased risk of infections
- Kidney problems
Tips
- You may be given Tylenol‚ (acetaminophen) and Benadryl‚ (diphenhydramine) or Claritin‚ (loratadine) before your infusion to reduce the risk of having an infusion reaction.
- If you are driving and/or Benadryl‚ makes you very drowsy, tell your nurse.
- Taking this medication may make you more susceptible to infections so you should avoid contact with sick people and wash your hands often
- Tell your physician, nurse or pharmacist if you have gained or lost any weight as this may change your dose.
- This medication is typically not given if you are pregnant.
- Always use birth control to prevent pregnancy while on this medication and speak with your physician or pharmacist before breastfeeding while on this medication.
- For information about birth control options, speak with your physician or pharmacist.
- Talk to your health care provider before receiving any vaccines.
- Some vaccines you should avoid while others may not work while on this medication.
When to contact your healthcare provider
If you are experiencing:
- Chest tightness, trouble breathing, wheezing
- Rash, hives, extreme itchiness
- Swelling of the face or lips and swelling or tingling of the tongue and throat
- High fever, severe sore throat or any other signs of infection
- Fast heartbeat (palpitations), sweating, confusion
- Loss of appetite, unusual tiredness or low-grade fever for more than 2 days
- Extreme headache, painful eye movements, difficulty tolerating bright light, or painful neck or head movements
- Although fetal and infant risk appear minimal if immune globulin is given to pregnant or breastfeeding women, you should contact your physician if you are or if you think you may be or if you would like to become pregnant or breastfeed an infant.
Brand Name
Trexall™, Rheumatrex®
What it is
An oral or self-injectable chemotherapy agent with immunosuppressant and anti-inflammatory properties approved for treating certain malignancies including leukemia, breast cancer and others. It's also approved for treating severe rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis.
What it does
- May delay the progression of multiple sclerosis
- May reduce relapse rates
How it works
Methotrexate produces immunosuppressive effects with high doses by inhibiting folic acid production. Folic acid is necessary for the synthesis of DNA and the reproduction of cells. With low, once-weekly dosing, its anti-inflammatory effects are utilized, resulting from the suppression of white blood cell activity.
How it's given
- Methotrexate is available in a pill form and in an injection form.
- The injectable form is usually supplied as a solution in a glass vial, so it does not have to be mixed but has to be drawn up before injecting.
- Methotrexate rarely may be supplied in a powder form. If you receive this product from your pharmacy, it will need to be mixed with the proper solution before drawing up. Speak with the pharmacist if this is the case.
- You will be instructed on this procedure by your physician or a nurse when starting therapy and will be given prescriptions for supplies when necessary and instruction on what additional materials you will need for this procedure.
- Typical Dose: 7.5 mg to 30 mg by mouth once weekly; doses are increased or decreased as needed
- Methotrexate is taken orally in a tablet form or injected subcutaneously (under the skin) or intramuscularly (in the muscle).
- A nurse or your physician should show you how to inject this medication.
- Your first, self-administered dose should be done under the direct supervision of an appropriately qualified health care practitioner.
- After the injection, dispose the syringe into a hard-welled, chemo-safe container.
Possible Side Effects
- Pain, redness, swelling, and irritation at the injection site
- Susceptibility to infection
- Nausea, vomiting, lack of appetite (more common with tablets)
- Mouth sores, headache, fever, chills
- Allergic reaction
- Itching, hives, swelling in your face or hands, chest tightness
- Lung disease
- Dry, non-productive (not coughing up sputum) cough
- Liver damage
- Pain in the upper, right area of your torso, yellow color of skin and eyes
- Blood disorders such as anemia or easy bruising or abnormal bleeding
- Increased sensitivity to sun or UV lights, skin color changes, hair loss
- Malignancies
- This risk may persist even after stopping this medication
Tips
- Do not stop taking this medication or change the dose or dosing schedule without speaking with your physician.
- Always call your refills in to your pharmacy before you are out of medication to avoid any disruption in therapy.
- If you miss a dose of your medication, take it as soon as you remember:
- You can resume your regular schedule the next week but don’t take doses within 3 days of each other.
- You will need to have your blood checked regularly for blood and liver damage and before beginning treatment.
- Always have your blood checked when schedules if requested by your physician.
- Limit the use of alcohol while taking methotrexate, which may put you at an increased risk of liver problems.
- This medication should not be used if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
- Always use birth control to prevent pregnancy while on this medication and speak with your physician or pharmacist before breastfeeding while on this medication.
- For information about birth control options, speak with your physician or pharmacist.
- If a couple is planning on becoming pregnant, both men and women receiving methotrexate should continue using contraceptives for 3 months after discontinuing methotrexate, before trying to conceive.
- Methotrexate will cause you to be more sensitive to sun
- Wear protective clothing while outdoors
- Wear sunscreen of at least SPF 30 on exposed areas
- Do not use sun lamps or booths
- Taking this medication may make you more susceptible to infections so you should avoid contact with sick people and wash your hands often.
- Before taking antibiotics such as Bactrim® or a penicillin (penicillin VK, amoxicillin, ampicillin, etc.) make sure your physician is aware that you are taking methotrexate as this may increase your risk of methotrexate toxicity.
- Make sure your physician is aware if you are taking an NSAID (i.e. Advil®, Motrin®, Aleve®) on a regular basis while on methotrexate as this may increase your risk of methotrexate toxicity.
- However, this is usually not a problem with low, once-weekly dosing.
- Talk to your health care provider before receiving any vaccines.
- Some vaccines you should avoid while others may not work while on this medication.
When to contact your healthcare provider
If you are experiencing:
- Chest tightness, trouble breathing, wheezing
- Rash, hives, blistering or severe itching
- Swelling of face, lips, tongue or throat
- High fever, severe sore throat or any other signs of infection
- Fast heartbeat, sweating, confusion
- Bruising, black, tarry stools, blood in urine
- You should not become pregnant or breastfeed an infant while using this medication.
- Contact your physician if you are or if you think you may be or if you would like to become pregnant or breastfeed an infant.
Brand Name
"Cytoxan®"
What it is
An injectable chemotherapy agent with immunosuppressant properties approved for treating certain malignancies including breast cancer, lung cancer, and several others.
What it does
- Lowers the number of white blood cells in your body
- May slow down the progression of progressive forms of multiple sclerosis
- May decrease the frequency and severity of relapses in patients with very aggressive forms of relapsing multiple sclerosis
How it works
- It decreases the amount of white blood cells in the blood
- The formation of white blood cells in the bone marrow is decreased
How it's given
- Intravenously – in the multiple sclerosis center infusion room
- Infused over 30 – 60 minutes. In addition, intravenous steroids and intravenous fluids will be infused over an additional 1-2 hours.
- Dose
- Based on body surface area
- Calculated using height and weight
- Most patients receive between 1000 – 3000 mg per dose
- Your dose may be adjusted based on the number of white blood cells in your blood
- Your physician will instruct you on how and when to have your blood checked after your infusion
- May be given for up to 3 years or longer. A typical administration schedule may be as follows:
- Once monthly for 1 year
- Once every 6 weeks for the second year
- Once every 8 weeks for the third year
Possible Side Effects
- Short-term
- Report any pain or discomfort near the IV site to your nurse
- Susceptibility to infection
- Nausea, vomiting, lack of appetite
- Mouth sores
- Headache, fever, chills
- Hair loss, skin and nail discoloration
- Irregular or loss of menstrual cycle
- Long-term
- Infertility – inability to become pregnant
- It is still very important to use birth control if you are sexually active as pregnancy may still occur
- Hemorrhagic cystitis – inflammation of the bladder
- This risk may persist even after stopping this medication
- Malignancies
- This risk may persist even after stopping this medication
- Impaired wound healing
Tips
- You will receive medication to prevent nausea before your infusion and a prescription for medication to be taken at home.
- It's usually easier to prevent nausea than it is to remove it once it is present so use your medication as prescribed even if you think you can tolerate the nausea without it.
- You must take in 3 liters of fluid after your infusion to prevent bladder problems.
- All or part of this can be given to you at the multiple sclerosis center as an intravenous infusion or you may drink all or part of this at home.
- Caffeinated beverages (soda, coffee) should be avoided
- You must also take in 3 liters of fluid on the day following your infusion.
- Try to avoid foods and smells that may trigger your nausea.
- Always have your blood checked as instructed to ensure proper dosing of your medication.
- Taking this medication may make you more susceptible to infections so you should avoid contact with sick people and wash your hands often.
- This medication should not be used if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
- Always use birth control to prevent pregnancy while on this medication and speak with your physician or pharmacist before breastfeeding while on this medication.
- For information about birth control options, speak with your physician or pharmacist.
- Cytoxan® therapy increases your risk for skin cancer
- Wear protective clothing while outdoors
- Wear sunscreen of at least SPF 30 on exposed areas
- Do not use sun lamps or booths
- Talk to your health care provider before receiving any vaccines.
- Some vaccines you should avoid while others may not work while on this medication.
When to contact your healthcare provider
If you are experiencing:
- Chest tightness, trouble breathing, wheezing
- Rash, hives or severe itching
- Swelling of face, lips, tongue or throat
- High fever, severe sore throat or any other signs of infection
- Fast heartbeat, sweating, confusion
- Nausea not controlled by your medication
- Blistering of peeling of you skin
- Pain when urinating or blood in your urine (pink urine)
- Extreme tiredness, abnormal bleeding or easily bruising
- You should not become pregnant or breastfeed an infant while using this medication.
- Contact your physician if you are or if you think you may be or if you would like to become pregnant or breastfeed an infant.
Brand Name
"Novantrone"
What it is
An injectable chemotherapy agent with immunosuppressant properties approved for treating certain malignancies and is the only currently approved medication for secondary-progressive multiple sclerosis. In addition, it is approved for treating worsening forms of relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis.
What it does
- Lowers the number of white blood cells in your body
- May reduce the progression of disability in secondary-progressive multiple sclerosis
- May decrease the frequency and severity of relapses in patients with relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis
How it works
- It decreases the amount of white blood cells in the blood
- The formation of white blood cells in the bone marrow is decreased
How it's given
- Intravenously – in the multiple sclerosis center infusion room
- Infused over 15 – 30 minutes
- Dose is based on body surface area, which is calculated using height and weight
- Most patients receive between 10 and 20 mg
- A single dose is given once every 3 months
- An echocardiogram must be performed prior to every infusion. Results must be sent to the MS Center prior to infusion.
- An echocardiogram must also be performed annually after treatment with Mitoxantrone has ended (FDA guidelines, July 2008).
Possible Side Effects
- Short-term
- Slight discoloration around or along the vein in which the drug is being infused; this may be ok or may indicate misplacement of your IV
- Immediately report any pain, discomfort or discoloration near the IV site to your nurse
- Susceptibility to infection
- Nausea, vomiting, lack of appetite
- Mouth sores
- Headache, fever, chills
- Temporary hair loss
- Temporary (2 – 3 days) bluish/green discoloring of the urine or the white part of the eye
- Irregular or loss of menstrual cycle
- Slight discoloration around or along the vein in which the drug is being infused; this may be ok or may indicate misplacement of your IV
- Long-term
- Cardiac (heart) toxicity
- You will be required to have a simple test done before each dose.
- An ultrasound of your heart called an echocardiogram allows your doctor to check for any damage.
- Infertility – inability to become pregnant
- It is still very important to use birth control if you are sexually active as pregnancy may still occur
- Malignancies, including increased risk of lymphoma.
- This risk may persist even after stopping this medication.
- Impaired wound healing
Tips
- You will receive medication to prevent nausea before your infusion and a prescription for medication to be taken at home.
- It's usually easier to prevent nausea than it is to remove it once it is present so use your medication as prescribed even if you think you can tolerate the nausea without it
- Avoid foods and smells that can trigger your nausea.
- Always keep your appointment for your echocardiogram.
- Taking this medication may make you more susceptible to infections so you should avoid contact with sick people and wash your hands often.
- This medication can make your urine, eyes and nails blue-green color.
- This is temporary and usually goes away within a couple days after your infusion.
- This medication should not be used if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
- Always use birth control to prevent pregnancy while on this medication and speak with your physician or pharmacist before breastfeeding while on this medication.
- For information about birth control options, speak with your physician or pharmacist.
- Talk to your health care provider before receiving any vaccines.
- Some vaccines you should avoid while others may not work while on this medication.
When to contact your healthcare provider
If you are experiencing:
- Chest tightness, trouble breathing, wheezing
- Rash, hives or severe itching
- Swelling of face, lips, tongue or throat
- High fever, severe sore throat or any other signs of infection
- Fast heartbeat, sweating, confusion
- Nausea not controlled by your medication
- Blistering of peeling of you skin
- Extreme tiredness, abnormal bleeding or easily bruising
- Shortness of breath or swelling of the ankles
- You should not become pregnant or breastfeed an infant while using this medication.
- Contact your physician if you are or if you think you may be or if you would like to become pregnant or breastfeed an infant.
Brand Name
Tysabri®
What it is
An injectable medication that is a manufactured antibody designed to prevent certain types of white blood cells from moving out of the bloodstream and into organs, namely the brain. Although it has been studied in patients with Crohn's disease, an autoimmune disease similar to multiple sclerosis in that the immune system is attacking the intestines, currently, natalizumab's only approved indication is for treating patients with active relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis.
What it does
In patients with relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis, natalizumab has been shown to delay the accumulation of physical disability and reduce the frequency of clinical exacerbations.
How it works
Natalizumab binds to a specific site, or receptor on T-cells and prevents them from binding to other specific receptors on the inside of blood vessels. T-cells normally rely on binding to these receptors in order to cross into the central nervous system. Inhibiting this interaction keeps the activated T-cells out of the central nervous system, preventing them from attacking the myelin sheath that covers brain and spinal cord nerve cells.
PML
The FDA approved Tysabri® in November of 2004. Biogen Idec and Elan stopped the use of all Tysabri® infusions in the public and in research studies in February 2005 because of reports of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML). PML is a rare neurological disease that is caused by the JC virus that can cause death or severe disability. There is no known cure for PML. This disease can affect people with a weakened immune system. Three patients, developed PML out of over 3000 that had received Tysabri® treatment in research studies. All of these patients that developed PML had received additional medications that suppressed the immune system either in combination, or just prior to the administration of Tysabri®. A full review of the safety data from Tysabri® studies in MS has now been completed. No new confirmed cases of PML were found. The decision to start using the drug again was based on the results of this safety evaluation. Any new information that might affect you or your treatment will be shared with you as soon as possible. Since the risk of developing PML exists, Tysabri® is generally recommended for patients whom have not responded adequately to, or who have not tolerated other treatments for MS. Patients receiving Tysabri® must be enrolled in the TOUCH™ Prescribing Program. During the second post-marketing phase, of Tysabri®, 2 new cases of PML were diagnosed in August 2008, out of a total of 6,600 patients who were treated for 18 months or longer. The risk of PML still remains at approximately 1/1000.
The TOUCH™ Prescribing Program
Tysabri® is only given by physicians and infusion centers that are enrolled in the TOUCH™ Prescribing Program with Biogen. The Partners MS Center and participating physicians are enrolled in the TOUCH™ Prescribing Program.
Once a physician at the Partners MS Center has deemed you an appropriate candidate to receive Tysabri®, you must read, discuss and understand the medication guide and all forms given to you regarding this medication.
Once approved through Biogen and your insurance, you may set up an appointment at the infusion center at 1 Brookline Place.
In order to start Tysabri® and at follow-up monitoring, you will need a:
- Neurological exam: before and about 3 months after you begin treatment
- MRI scans: before and every 6 months while on treatment
- Regular exams with your physician every 6 months per our standard care
Before every infusion an infusion nurse will ask you questions regarding your health and medications.
How it's given:
- Intravenously – in the multiple sclerosis center infusion room
- Infused over 60 minutes followed by a 60 minute observation period
- Dose
- 300 mg every four weeks
Warning: Tysabri® should not be used in patients who have or have had PML or have a condition that weakens the immune system:
- HIV infection or AIDS, leukemia or lymphoma, or an organ transplant, and others
Warning: Tysabri® should not be used in combination with:
- Any investigational (research) treatment
- Other monoclonal antibodies (i.e. Zenapax, Rituxan)
- IV immunoglobulin (IVIg or IgG)
- Plasmapheresis or cytapheresis
- Total lymphoid irradiation
- T-cell or T-cell receptor vaccination
- Immunosuppressive medications (Cytoxan, methotrexate, cladribine)
- Immunomodulatory treatments:
- Avonex (interferon beta-1a)
- Rebif (interferon beta-1a)
- Betaseron (interferon beta-1b)
- Copaxone (glatiramer acetate or co-polymer-1)
Possible Side Effects
- Itching, hives, swelling in your face or hands, chest tightness, low blood pressure
- Headache, nausea, diarrhea, stomach pain
- Fatigue, trouble sleeping, depression
- Dizziness or tremor
- Difficulty urinating
- Increased risk of PML
- Increased risk of other infections and infection outbreaks
- Urinary tract infections, vaginitis, lung infections, herpes zoster (shingles), herpes outbreaks
- Arm and leg pain, joint pain
- Liver damage
- pain in the upper, right area of your torso, yellow skin and eyes
- Irregular, reduced or loss of menstruation
- Appendicitis; rare
- Melanoma; rare
- Report to your physician any significant changes in the size, shape or color of any moles on your body
- Report any pain or discomfort near the IV site to your nurse
- Allergic reaction – typically occurs within 2 hours of the start of the infusion, but may happen several hours after
Tips
- Always bring an updated list of your current medications to your physician or infusion appointment and show it to your physician, nurse or pharmacist.
- Tell all of your physicians that you are taking Tysabri®.
- Always have your blood drawn when your physician requests it.
- Taking this medication may make you more susceptible to infections so you should avoid contact with sick people and wash your hands often.
- This medication should not be used if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
- Always use birth control to prevent pregnancy while on this medication and speak with your physician or pharmacist before breastfeeding while on this medication.
- For information about birth control options, speak with your physician or pharmacist.
- Talk to your health care provider before receiving any vaccines.
- Some vaccines you should avoid while others may not work while on this medication.
When to contact your healthcare provider
- If you have any new or suddenly worsening neurological symptoms that keep getting worse and affect your thinking, eyesight, balance or strength:
- You must contact your physician within 48 hours
- You may need to visit the clinic within 5 days of the start of the symptoms. If your physician feels it is necessary, you may need to have these tests done:
- Neurological exam
- MRI with and without gadolinium dye
- An injection into an arm vein of gadolinium (a "dye") during the MRI scan. The gadolinium helps us see the changes from MS more clearly.
- Blood and urine collection
- Lumbar puncture. This procedure is to remove a small sample of cerebral spinal fluid from your lower spine. A hollow needle is inserted between the vertebrae (backbones) in the lower back and into the space that contains the spinal fluid. We may need to collect this fluid to test for the JC virus. A lumbar puncture takes approximately 30 minutes and is done using a local anesthetic. The physician will do it here in the clinic and full explanation will be given.
- If you are diagnosed with a medical condition that weakens your immune system.
- If you start taking medications that may weaken your immune system.
- If you are experiencing:
- New neurological symptoms such as new weakness, numbness, change in vision, change in speech or cognition, imbalance or dizziness.
- Chest tightness or pain, trouble breathing, wheezing
- Rash, hives, extreme itchiness
- Swelling of the face or lips and swelling or tingling of the tongue and throat
- High fever, severe sore throat or any other signs of infection
- Fast heartbeat (palpitations), sweating, confusion
- You should not become pregnant or breastfeed an infant while using this medication.
- Contact your physician if you are or if you think you may be or if you would like to become pregnant or breastfeed an infant.
Brand Name
"Rituxan"
What it is
An injectable chemotherapy agent with immunosuppressant properties approved for treating certain malignancies including Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and certain types of leukemia. It's also been used for treating lupus and rheumatoid arthritis.
What it does
In patients with relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis, rituximab has been shown to reduce MRI measured activity of lesions and to reduce the number of relapses. It may also decrease progression to disability.
How it works
Rituximab binds to a site or receptor on the surface of certain white blood cells, specifically B-cells and specifically to the CD20 receptor. This results in the elimination of B-cells from the body that lasts for up to a year.
How it's given
- Intravenously – in the multiple sclerosis center infusion room
- Infused slowly over several hours
- The usual treatment regimen is: 1000 mg x 2 doses, given 2 weeks apart
- For example: 1000mg on December 1st and 1000mg on December 15th. This "cycle" is given once a year
Possible Side Effects
- Report any pain or discomfort near the IV site to your nurse
- Allergic reaction
- Itching, hives, swelling in your face or hands, chest tightness
- Headache, nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, cough
- Fatigue, trouble sleeping
- Dizziness, tremor, or changes in vision
- Difficulty urinating
- Increased risk of infections, including progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML)
- Impaired wound healing
- Difficulty walking or loss of coordination
- Cardiac arrhythmia: palpitations, shortness of breath
- Blood disorders such as anemia or easy bruising or abnormal bleeding
Tips
- You may be given Tylenol‚ (acetaminophen) and Benadryl‚ (diphenhydramine) or Claritin‚ (loratadine) before your infusion to reduce the risk of having an infusion reaction.
- If you are driving and/or Benadryl‚ makes you very drowsy, tell your nurse.
- Taking this medication may make you more susceptible to infections so you should avoid contact with sick people and wash your hands often.
- Tell your physician, nurse or pharmacist if you have gained or lost any weight as this may change your dose.
- You may experience a reaction during the infusion (fever, chills, or change in blood pressure)
- You will be closely monitored during the infusion by nurses but report any unusual symptoms if they occur.
- This medication should not be used if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
- Always use birth control to prevent pregnancy while on this medication and speak with your physician or pharmacist before breastfeeding while on this medication.
- For information about birth control options, speak with your physician or pharmacist.
- Talk to your health care provider before receiving any vaccines.
- Some vaccines you should avoid while others may not work while on this medication.
When to contact your healthcare provider
If you are experiencing:
- Chest tightness, trouble breathing, wheezing
- Rash, hives, extreme itchiness
- Swelling of the face, lips, tongue or throat
- High fever, severe sore throat or any other signs of infection
- Fast heartbeat (palpitations), sweating, confusion
- Changes in vision, difficulty walking or loss of coordination
- Bruising, black and tarry stools, blood in urine
- You should not become pregnant or breastfeed an infant while using this medication.
- Contact your physician if you are or if you think you may be or if you would like to become pregnant or breastfeed an infant.
What it is
Daclizumab (Zinbryta) is an FDA approved medication for the treatment of relapsing remitting MS.
What it does
In clinical trials, Daclizumab therapy led to a 50% or more reduction in annual MS disease relapse and MRI activity compared to placebo or interferon beta in clinical trials
How it works
Originally developed as a prophylactic agent against solid organ allograft rejection, this humanized monoclonal antibody selectively targets the IL-2 receptor and inhibits activated T cell signaling.
How it's given
Daclizumab is a once a month subcutaneous injection
Possible Risks and Side Effects
- Daclizumab should generally be used only in patients who have had an inadequate response to two or more MS drugs because daclizumab has some serious safety risks, including liver injury and immune conditions. Because of the risks, daclizumab has a boxed warning and is available only through a restricted distribution program
- The boxed warning tells prescribers that the drug can cause severe liver injury. Your doctor should perform blood tests to monitor your liver function prior to starting daclizumab, monthly before each dose, and for up to six months after the last dose.
- Daclizumab can also cause inflammation of the colon (non-infectious colitis), skin reactions, and enlargement of lymph nodes (lymphadenopathy).
- Finally, some patients may have hypersensitivity reactions (anaphylaxis or angioedema) with the injections, and may experience increased risk of infections, and symptoms of depression and/or suicidal ideation.
- The most common adverse reactions reported by patients receiving daclizumab in the clinical trial that compared it to Avonex (interferon beta-1a) include cold symptoms (nasopharyngitis), upper respiratory tract infection, rash, influenza, dermatitis, throat (oropharyngeal) pain, eczema, and enlargement of lymph nodes.
- The most common adverse reactions reported by patients receiving daclizumab when compared to placebo were depression, rash, and increased alanine aminotransferase (AST) – a liver enzyme.
Brand Name
CellCept, Myfortic
What it is
An oral immunosuppressant that is approved for preventing rejection in patients receiving solid-organ transplants. In addition to multiple sclerosis, it has been successfully used off-label for treating lupus, certain types of skin diseases, and other immune related conditions.
What it does
CellCept® is usually given in combination with other medications to patients with relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis. Small studies have shown that it may decrease the amount of relapses and may slow the progression of the disease.
How it works
It inhibits an enzyme in the body that is necessary for the production of specific purines. These specific purines are necessary for certain white blood cells, specifically T- and B-cells, to carry out an attack against offending material. This leads to less damage of myelin and neurons in the brain.
How it's given
- Orally – two forms exist but they are not equivalent in dosing. Currently, CellCept® is the brand that is typically used for multiple sclerosis.
- Both forms of mycophenolate should be taken one hour before or two hours after food intake for proper absorption.
- Tablets should not be crushed, chewed, or cut and capsules should not be opened prior to ingesting. Tablets and capsules should be swallowed whole.
- CellCept® – mycophenolate mofetil capsules and tablets typical dosing regimen:
- 250 mg by mouth twice daily for week 1 then,
- 500 mg by mouth twice daily for week 2 then,
- 750 mg by mouth twice daily for week 3 then,
- 1000 mg by mouth twice daily, thereafter
- Myfortic – mycophenolate sodium delayed-release tablets
- 720 mg by mouth twice daily on an empty stomach
- If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember but do not double up with the next dose.
Possible Side Effects
- Short-term
- Increased risk of infection, including progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML)
- Nausea, stomach pain, diarrhea
- Increasing the dose slowly reduces these effects
- These effects may return for a day or two when doses are increased
- Weakness
- Dizziness, difficulty sleeping
- Long-term
- Malignancies: skin, lymphoma. This risk may persist even after stopping this medication
- Ulcers or stomach bleeding
Tips
- Increasing the dose slowly will lessen the incidence of side effects.
- If you still experience stomach side effects realize that these do get better over time, even though they may reappear while increasing the dose.
- Avoid taking antacids containing aluminum or magnesium (i.e. Maalox®, Mylanta®) at the same time as mycophenolate as these will affect how much drug you absorb. It should be taken at least one hour before or two hours after taking antacids.
- Some medications used to lower cholesterol such as cholestyramine should not be taken if you are taking mycophenolate, as they will inhibit your absorption of the medication regardless of when you take them. Tell your physician if you are taken cholestyramine or a similar medication.
- Avoid taking calcium supplements or iron supplements at the same time as mycophenolate as these will affect how much drug you absorb. It should be taken at least one hour before or two hours after taking these supplements.
- Avoid taking antacids containing aluminum or magnesium (i.e. Maalox®, Mylanta®) at the same time as mycophenolate as these will affect how much drug you absorb. It should be taken at least one hour before or two hours after taking antacids
- Tell your physician if you are taking Zovirax® (acyclovir) while taking mycophenolate as this may increase its levels and you may have to have your blood checked while on both.
- Birth control pills may not work while taking mycophenolate so couples should use alternate forms of birth control during mycophenolate therapy and for 6 weeks after stopping therapy. If you are or think you may be pregnant, notify your physician immediately.
- Always have your blood checked when schedules if requested by your physician.
- You might be at a higher risk for certain skin cancers.
- Exposure to sunlight and UV light should be limited by wearing protective clothing and using a strong sunscreen (at least SPF-30) when you are outdoors.
- Avoid sunlamps and tanning beds.
- Talk to your health care provider before receiving any vaccines.
- Some vaccines you should avoid while others may not work while on this medication.
- Taking this medication may make you more susceptible to infections so you should avoid contact with sick people and wash your hands often.
- Do not stop taking this medication or change the dose or dosing schedule without speaking with your physician.
- Always call your refills in to your pharmacy before you are out of medication to avoid any disruption in therapy.
- This medication should not be used if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
- Always use birth control to prevent pregnancy while on this medication and speak with your physician or pharmacist before breastfeeding while on this medication.
- For information about birth control options, speak with your physician or pharmacist.
When to contact your healthcare provider
If you are experiencing:
- Chest tightness, trouble breathing, wheezing
- Rash, hives or severe itching
- Swelling of face, lips, tongue or throat
- High fever, severe sore throat or any other signs of infection
- Fast heartbeat, sweating, confusion
- Tell your physician if you have any uncontrolled digestive system conditions
- High fever, severe sore throat or any other signs of infection
- If your stool is very black or you see blood in your stool
- Extreme tiredness, abnormal bleeding or easily bruising
- You should not become pregnant or breastfeed an infant while using this medication.
- Contact your physician if you are or if you think you may be or if you would like to become pregnant or breastfeed an infant.
Brand Name
Gilenya
What it is
A disease-modifying oral agent that is indicated to reduce the frequency of MS exacerbations and to delay the progression of physical disability in patients with relapsing forms of MS.
What it does
Gilenya is a disease-modifying drug used as monotherapy to reduce exacerbations and accumulation of disability in relapsing forms of MS. Two major clinical trials were done to assess the efficacy and safety of the drug. One tested Gilenya versus a placebo, the other tested Gilenya versus interferon. One trial demonstrated a significant delay in disability progression and both trials showed a significantly lower relapse rate.
How it works
The mechanism of Gilenya is not fully understood. It binds to receptors in the body that block progression of lymphocytes (white blood cells) into the blood and may reduce the movement of lymphocytes into the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). Lymphocytes are part of the auto-immune response in MS; they play a role in inflammation and the demyelination (removal of protective covering) of axons.
How it's taken
- Orally
- Gilenya 0.5 mg orally once daily.
- Take the tablet whole. Do not break, crush, chew, or dissolve before swallowing as this may increase the risk for side effects.
- May be taken with or without food.
- Do not discontinue Gilenya without first talking to your physician.
- If you miss a dose, take when you remember, but if it is too close to the next dose DO NOT DOUBLE UP. You will be monitored for six hours after the first dose for signs of bradycardia (slow heart rate).
- If you are taking an anti-arrhythmic medication (including calcium channel blockers and beta-blockers) or have other cardiac risk factors such as congestive heart failure an EKG will be obtained prior to beginning therapy.
- If you have not had chickenpox before or a varicella zoster virus (VZV) vaccine, you may be tested for antibodies to VZV. If you do not have antibodies to VZV, you may be asked to receive the vaccination prior to starting therapy.
- A complete blood count, bilirubin, and liver function tests will be obtained before initiation of therapy.
- An eye exam will be administered before initiation of therapy and 3-4 months into therapy.
Possible Side Effects
- Common
- Headache
- Influenza (flu)
- Diarrhea
- Back pain
- Cough
- Increase in liver enzymes
- Serious
- Infections
- AV block and bradyarrhythmia
- Macular Edema
- Leuokopenia
All side effects should be reported to your physician. You may report side effects to the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Tips
- If discontinued for more than two weeks, re-initiation of therapy will require another six-hour monitoring period after the re-initiation dose.
- Certain vaccines should be avoided while on Gilenya and two months following discontinuation of therapy.
- Gilenya greatly increases your risk of infections. Report any signs of infection (fever, sore throat, cough, etc) to your healthcare provider.
- Gilenya may cause macular edema; a serious condition of the eye. Please notify your physician of any changes in vision. If you are diabetic or have a history of uveitis, your risk is increased.
- Inform your physician if you have any shortness of breath.
- Gilenya may affect your liver enzymes. Inform your doctor if you have any nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, weight loss, yellowness of eyes, or dark urine.
- Do not change the dose or dosing schedule without speaking with your physician.
- Animal studies of Gilenya have demonstrated harm to the fetus. Effective birth control is recommended while taking Gilenya and two months after discontinuing.
- Gilenya remains in your system two months after discontinuation. Lymphocytes may continue to be low during these two months.
- Notify your physician and pharmacist before starting any new prescription medications, over the counter medications or herbal supplements. Certain heart medications and anti-fungal drugs may strongly interact with Gilenya and need to be monitored.
- Your progress with this drug will need to be monitored. It is important to keep all scheduled appointments.
Pregnancy Risk
- Gilenya is classifed as pregnancy risk category C, which means there are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Animal studies demonstrated fetal toxicity. Women taking this medication should practice adequate birth control.
- Gilenya should be stopped for at least 2 months prior to conceiving.
When to contact your healthcare provider
- If you become pregnant
- If you are experiencing or have experienced:
- Allergic reaction: Itching or hives, swelling in your face or hands, swelling or tingling in your mouth or throat, chest tightness, trouble breathing.
- Any signs of infection (fever, sore throat, cough, etc.)
- Changes in vision
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, weight loss, yellowness of eyes, dark urine
Who to contact
For problems or concerns please call the MS Center at 617-525-6550 Monday through Friday 9:00am - 5:00pm. During off-hours, please call the on-call doctor at 617-732-5656 then beeper #11378.
Brand Name
Aubagio
What it is
Aubagio (teriflunomide) is a once a day oral pill that was approved by the FDA September 12, 2012 for use in relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis.
What it does
In a phase III trial, TEMSO, compared to placebo the higher dose of Aubagio (14mg) reduced relapse rate 31%, 3 month disability progression 30%, and total MRI lesion volume 67%.
How it works
Teriflunomide acts in multiple sclerosis by reducing white blood cells through effects on DNA synthesis.
How it's given
Teriflunomide is a daily pill. It is available in doses of 7mg and 14mg. There is a better effect on the disease if patients taking the 14mg dose and the side effect profile is comparable between the two
Storage
- Room temperature
Possible Side Effects
- Patients taking this drug were potentially more susceptible to hair loss (13% vs 3% in placebo), diarrhea (18% vs. 9% in placebo) and nausea (14% vs. 7% placebo) Serious effects on the fetus have been seen with a drug similar to Aubagio, leflunomide, which might apply to Aubagio as well. For this reason the FDA has recommended not taking this drug within two years of trying to conceive a child unless a wash out procedure is performed. Because the drug may potentially cross into the sperm this also applies to men.
- A TB test should be performed prior to starting this drug as should basic bloodwork.
- Because mild liver irritation or damage (57% vs. 36% placebo) can occur blood is monitored monthly for six months.
Tips
- Do not stop taking this medication or change the dose or dosing schedule without speaking with your physician.
- This medication should not be used if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Always use birth control to prevent pregnancy while on this medication and speak with your physician or pharmacist before breastfeeding while on this medication.
For information about birth control options, speak with your physician or pharmacist.
Brand Name
Tecfidera®
What it is
A disease-modifying oral agent that is indicated to reduce the frequency of MS relapses and to slow the worsening of physical disability in patients with relapsing forms of MS.
What it does
Dimethyl fumarate is a disease-modifying drug used as monotherapy to reduce exacerbations and accumulation of disability in relapsing forms of MS. There were two major trials to assess the safety and efficacy of the drug. In one trial, dimethyl fumarate was tested versus a placebo. In another, dimethyl fumarate and glatiramer acetate (Copaxone) were tested versus a placebo. Both trials demonstrated a reduced relapse rate and a reduction in lesions detectable by MRI. One trial demonstrated a delay in disability progression. In the second trial, dimethyl fumarate demonstrated greater relapse reduction and MRI lesion reduction than glatiramer acetate.
How it works
The mechanism of dimethyl fumarate is not fully understood. The proposed mechanism is that it reduces cellular stress in the body. By reducing this stress, dimethyl fumarate may lessen the inflammatory response that occurs in MS.
Most importantly:
We recommend starting the medication according to the following schedule:
- Week 1+ 2
- 120mg once a day after large meal
- Week 3 + 4
- 240mg once a day after large meal
- Week 5
- 240mg after breakfast and 240mg after dinner
- Week 6 and beyond
- Continue at the week 5 dose
In order to minimize gastrointestinal discomfort and flushing. You should always take the medication with food.
For the first month take a tablespoon of peanut butter 5 minutes prior to taking the medication.
Recommendation:
- Healthy alternative to peanut butter: nuts, peanut butter, fatty fish, avocados, flaxseed, tofu, olive oil)
- Take 81mg aspirin (not enteric coated) 30 minutes before if flushing occurs. May take for about 4-6 weeks and then check with your doctor if flushing continues.
- Take Pepto-Bismol/Kaopectate for nausea/diarrhea
- Stop any medication used for bowel regulation. If Tecfidera does not affect your GI system, you may resume.
- Take the capsule whole. Do not crush, chew, or open contents.
- Call your doctor if you experience persistent flushing or stomach problems.
- Do not discontinue dimethyl fumarate without first talking to your physician.
- If you miss a dose, take it when you remember, but if it is too close to the next dose DO NOT DOUBLE UP.
- A complete blood count will be obtained before initiation of therapy and at regular intervals during therapy.
Possible Side Effects
- Common
- Diarrhea
- Flushing
- Itching
- Nausea
- Rash
- Stomach pain
- Vomiting
- Serious
- Lymphocytopenia
All side effects should be reported to your physician. You may report side effects to the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Tips
- Although it is a rare side effect, dimethyl fumarate may decrease a particular type of white blood cells called lymphocytes. These cells are responsible for fighting infection in your body. Take extra care to maintain hygiene and wash hands as regularly as possible. Report any signs of infection (fever, sore throat, cough, etc.) to your healthcare provider.
- Animal studies of dimethyl fumarate have demonstrated harm to the fetus. Effective birth control is recommended while taking dimethyl fumarate.
- Notify your physician and pharmacist before starting any new prescription medications, over the counter medications or herbal supplements.
- Your progress with this drug will need to be monitored. It is important to keep all scheduled appointments.
When to contact your healthcare provider
- If you become pregnant
- If you are experiencing or have experienced:
- Allergic reaction: Itching or hives, swelling in your face or hands, swelling or tingling in your mouth or throat, chest tightness, trouble breathing.
- Any signs of infection (fever, sore throat, cough, etc.)
Who to contact
- For problems or concerns please call the MS Center at 617-525-6550 Monday through Friday 9:00am – 5:00pm.
- During off-hours, please call the on-call practitioner at 617-732-5656 then beeper #11378.
On March 28th 2017, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the humanized monoclonal antibody ocrelizumab (Ocrevus) for both relapsing multiple sclerosis (RRMS) and primary progressive multiple sclerosis (PPMS) in adults.
Have there been clinical trials?
The drug's approval was based on results from several clinical trials including OPERA 1 & 2 and ORATORIO phase 3 trials. The first two trials each included about 800 patients with RRMS who received intravenous ocrelizumab or the subcutaneous interferon b-1a Rebif®. Ocrelizumab demonstrated superior efficacy on the three major markers of disease activity; it reduced relapses per year by nearly half, slowed the worsening of disability and significantly reduced MRI lesions compared with Rebif® over a 2 year period (T1 gadolinium lesion reduction 94% and 95% in RRMS trials.)
ORATORIO included 732 patients with PPMS who received the treatment or matching placebo. PPMS patients on the medication were about 25% less likely to have their disability worsen.
How does it work?
Ocrelizumab is humanized monoclonal antibody designed to selectively target CD20-positive B cells, a specific type of immune cell thought to be a key contributor to the MS disease process. It works in a similar way to rituximab (Rituxan).
When will it be available?
We are very excited to have this as an option to offer to patients. However, we will be unable to administer this medication until we receive the medication from the drug company, Genentech. Then, the medication must be approved and available though our hospital pharmacy. We hope to be able to provide this medication as soon as possible.
How is the medication administered?
This medication will be given in the infusion center. You will have a dose of 300mg then 300mg two weeks later. After that, you will receive a 600mg dose every 6 months.
What labs will be checked before starting?
Before your first infusion we will routinely check the following labs:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC)
- Hepatitis Serologies (HBsAg, anti-HBV, HbcAb)
- Serum protein electrophoresis (SPEP)
Before re-dosing, every 6 months we will check:
- CD 19 count
- CBC
- SPEP
Your doctor may also check:
- JCV Ab titer
- Liver function tests (LFTs)
- CD20
- Tuberculosis test (TB quantiferon)
- HIV
- Pregnancy (hCG)
Additional screening tests will be considered at the discretion of the prescribing physician.
Cladribine (Mavenclad®)
- Brand name: Mavenclad®
- Generic name: Cladribine
- Dosing formulation: Oral Tablets, 10mg each
- Tablets can be stored at room temperature and taken at home. The medication is cytotoxic, which means you should keep the tablets in their container until just prior to taking them, and wash hands after taking the medication.
- Dosing instructions:
- The total dose of cladribine is 3.5 mg per kg. For example, a 100kg person will take 350 mg of cladribine in total. This is split over 2 years ("courses"), for 2 weeks each year ("cycles").
- Patients take the oral tablets daily for 4 to 5 days, and then one month later they will take tablets for another 4 to 5 days. One year later, this process is repeated.
- Bloodwork is done prior to starting each treatment year, and 6 months after each dose.
- Many patients need no further treatments; however, it can be repeated if needed.
Dosing schedule:
Treatment Year 1: Course 1
| Bloodwork | 4-5 tablets | 4-5 tablets | Bloodwork |
|---|---|---|---|
| Week 0 (Prior to starting) |
Week 1: Cycle 1 (Month 1) |
Week 5: Cycle 2 (Month 2) |
Week 26 (Month 6) |
Treatment Year 2: Course 2
| Bloodwork | 4-5 tablets | 4-5 tablets | Bloodwork |
|---|---|---|---|
| Week 48-52 (Prior to next course) |
Week 52: Cycle 1 (Month 12) |
Week 56: Cycle 2 (Month 13) |
Week 78 (Month 18) |
What is cladribine?
- Cladribine (Mavenclad®) is an oral medication approved by the FDA March 29, 2019 to treat relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS). This includes patients with relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS) as well as active secondary progressive MS (SPMS).
- The drug is a "purine analogue", which means that it looks similar to a purine, an important molecule used in DNA. Since cladribine is different than the natural purine molecule, rapidly dividing cells are halted, which leads to cell death. In the case of MS, the cells that we want to get rid of are the lymphocytes, which are white blood cells that are incorrectly attacking the brain and spinal cord. By killing this population of lymphocytes, the effects of cladribine can last for a long time.
- Prior to the approval of cladribine for MS, cladribine was approved by FDA as a treatment for certain hematologic malignancies, or blood cancers, though at different doses and given intravenously as opposed to oral tablets.
- Three randomized controlled trials have been performed to test cladribine tablets, including an extension study, summarized below.
What are the side effects of cladribine?
- Commonly reported: Headaches, nausea, dizziness.
The main effect of cladribine is "lymphopenia", or reduction in the number of lymphocytes. Since these cells are incorrectly attacking the brain and spinal cord in patients with MS, the number of relapses is less; however, these cells also prevent infections in our body, so patients on cladribine can have higher chance of infection.
- These may be urinary tract infections, respiratory infections, or viral infections including varicella zoster, which causes shingles. Medication to prevent shingles is recommended depending on blood count levels.
- Hepatitis is a viral infection that can cause liver injury, so prior to treatment hepatitis B and C are tested for.
- Live attenuated vaccines, including vaccination for varicella zoster and Hepatitis B are recommended to be completed 4 to 6 weeks prior to starting cladribine.
- If you have active infection, including hepatitis B and C, tuberculosis, or HIV, cladribine is not recommended.
Blood counts and liver testing. To monitor for lymphopenia, and liver injury, bloodwork is checked before starting as well as every 6 months while on cladribine, and 6 months after the last dose.
Heart failure. There is a rare risk of heart failure with cladribine. If you have a history of heart failure, or develop swelling of the legs, shortness of breath, or dizziness to the point of fainting while taking cladribine, seek medical advice.
Lymphocytes also are involved in monitoring the body for cancer, so patients taking cladribine may have an increased risk of cancer.
- The original randomized controlled trial of cladribine tablets versus placebo showed that out of 430 patients who received 3.5mg/kg of cladribine, three (0.7%) developed cancer compared with no patients who received placebo (Giovannoni, NEJM, 2010). This led to a delay in the approval of cladribine for MS.
- A subsequent metanalysis of eleven trials of various treatments in MS showed no increased rate of cancer from cladribine, but rather a lower rate of cancer in the specific placebo group from the original cladribine trial (Pakpoor, Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm, 2015). This finding led to the approval of cladribine tablets for MS.
- We still recommend regular cancer surveillance and do not recommend cladribine in patients with active (untreated or currently treated) cancer.
- Rapidly dividing cells are not only the lymphocytes. During pregnancy, the developing baby’s cells are rapidly dividing as well.
- For this reason, patients who are pregnant, or may become pregnant cannot take cladribine. A pregnancy test is required before starting.
- Both women and men should use reliable contraception if they are considering cladribine as it may interfere with sperm production as well. Contraception is continued for at least 6 months after the final cladribine dose.
Breastfeeding. It is not recommended to breastfeed until 10 days after the last dose. This recommendation is based on potential risk, there is no evidence that cladribine is excreted in the breast milk.
How effective is cladribine?
Cladribine is considered one of the "higher efficacy" medications, meaning that cladribine reduces the number of relapses, new MRI lesions, and potentially disability progression, more so than many other treatments for MS. This leads to higher risk of adverse events, as outlined above. Given this higher risk, and also higher effectiveness, cladribine is typically reserved for patients who continue to have disease activity despite being on a medication for MS, as opposed to being the first medication used. Three randomized controlled trials, as well as one extension trial, have been published to date (2021) that investigated cladribine.
Trial 1: CLARITY (Giovannoni, NEJM, 2010)
- This trial compared three groups: 433 patients with cladribine 3.5mg/kg; 456 patients with cladribine 5.25 mg/kg; and 437 patients who got placebo. These patients were followed for 96 weeks (2 years).
- Relapse rates. There was a 58% reduction in relapse rate for patients who were given cladribine compared to placebo. No relapses occurred in 81% of patients who received cladribine and 63% of patients who received placebo, during the 96-week (2 year) trial period.
- MRI lesions. In the 2-year trial, no patients given cladribine developed new MRI lesions, compared with an average of 0.67 new lesions per patient in the placebo group.
- Disability worsening. Worsening disability was observed in 13% of the patients treated with cladribine compared with 19% of the patients who received placebo.
- The higher dose of cladribine (5.25 mg/kg) was no better than the approved dose (3.5mg/kg) but had more reported side effects, specifically lymphopenia.
Trial 2: ORACLE MS (Leist, Lancet Neurol, 2014)
- This trial also compared three groups of patients who were randomized >after their first clinical attack: 206 patients with cladribine 3.5mg/kg; 204 patients with cladribine 5.25 mg/kg; and 206 patients who got placebo. These patients were followed for 96 weeks (2 years).
- Four malignancies occurred in the cladribine groups compared with 6 in the placebo groups, in this study.
- This trial showed that either dose of cladribine delayed the time to a second clinical attack.
Trial 3: ONWARD (Montalban, Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm, 2018)
- This 96-week trial randomized patients with either RRMS or SPMS, who were on interferon beta-1a and had a relapse or new MRI lesion, to either get cladribine in addition to their interferon beta-1a, or a placebo either their interferon beta-1a. Originally, patients could have received 3.5 mg/kg of cladribine or 5.25 mg/kg of cladribine, but since the efficacy of these doses had been shown equivalent the investigators amended their protocol to only provide 3.5 mg/kg as the trial was ongoing.
- Relapse rates. Patients who received cladribine in addition to interferon were 63% less likely to have further MRI lesions than those who received placebo plus interferon.
- MRI lesions. Patients who received cladribine in addition to interferon were 59% less likely to have further MRI lesions than those who received placebo plus interferon.
- Disability worsening. Patients had similar risk of developing disability worsening regardless if they were given cladribine or placebo, in addition to continuing interferon beta-1a.
Extension Trial: CLARITY-Extension (Giovannoni, Mult Scler, 2018)
- In this extension, patients who originally got placebo were given 3.5mg/kg cladribine, and the ones who received cladribine in the initial study were randomized to another 2 years of cladribine, or placebo. The safety and efficacy were similar, between 75-80% of patients remained free of relapses, MRI lesions, and worsening disability.
- Therefore, if needed, 2 additional courses of cladribine can be safely provided. At the same time, some patients remain disease-free after the first 2 courses only.
For more information please see the following websites and references:
- FDA label:
- Mavenclad® patient website:
References:
- Giovannoni et al. A Placebo-Controlled Trial of Oral Cladribine for Relapsing Multiple Sclerosis. N Engl J Med 2010; 362:416-426. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0902533.
- Giovannoni et al. Safety and efficacy of cladribine tablets in patients with relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis: Results from the randomized extension trial of the CLARITY study. Multiple Sclerosis Journal 2018, Vol. 24(12) 1594–1604. doi: 10.1177/1352458517727603.
- Leist et al. Effect of oral cladribine on time to conversion to clinically definite multiple sclerosis in patients with a first demyelinating event (ORACLE MS): a phase 3 randomised trial. Lancet Neurol. 2014 Mar;13(3):257-67. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70005-5.
- Montalban et al. Cladribine tablets added to IFN-β in active relapsing MS: The ONWARD Study. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm 2018;5:e477. doi:10.1212/NXI.0000000000000477.
- Pakpoor et al. No evidence for higher risk of cancer in patients with multiple sclerosis taking cladribine. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2015 Oct 1;2(6):e158. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000000158.
- Patti et al. Long-term effectiveness in patients previously treated with cladribine tablets: a real-world analysis of the Italian multiple sclerosis registry (CLARINET-MS). Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2020 Jun 10;13:1756286420922685. doi: 10.1177/1756286420922685.
Ozanimod (Zeposia®)
Medication Information:
- Brand name: Zeposia®
- Generic name: Ozanimod
- Dosing formulation:
- 0.92mg daily oral capsules, 0.23mg and 0.46mg initial capsules
- Capsules can be stored at room temperature and taken at home.
- Dosing instructions:
- An initial 7-day titration schedule is done, followed by one 0.92mg capsule daily
- Prior to starting ozanimod, bloodwork, an eye exam to look for macular edema, and an electrocardiogram (ECG) will be done, as well as checking for immunity to varicella zoster virus (VZV) and if needed vaccination.
Dosing schedule:
| Days 1 to 4 | Days 5 - 7 | Day 8 and thereafter |
|---|---|---|
| 0.23mg capsule once daily | 0.46mg capsule once daily | 0.92mg capsule once daily |
What is ozanimod?
- Ozanimod (Zeposia®) is an oral medication approved by the FDA to treat relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis on March 26, 2020. This includes patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS), clinically isolated syndrome (CIS), as well as active secondary progressive multiple sclerosis (SPMS).
- The drug is a "sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) receptor modulator", which means that it changes the way S1P receptors function inside your body. The result is that lymphocytes, which are white blood cells that are incorrectly attacking the brain and spinal cord in patients with multiple sclerosis, are unable to leave the lymph nodes, potentially preventing them from having access to the brain and spinal cord. Therefore, stopping this medication suddenly may result in "rebound activity", or recurrence or worsening of MS symptoms, so do not stop taking this medication without informing your provider.
- Other S1P receptor modulators include fingolimod (GIlenya®) and siponimod (Mayzent®), each with slight differences. Unlike the other S1P receptor modulators, ozanimod does not require observation for the first dose.
- Ozanimod is also approved in the treatment of Ulcerative Colitis
- Two randomized controlled studies tested ozanimod, (SUNBEAM, and RADIANCE, summarized below) to determine that ozanimod is more effective than interferon at reducing MS relapses and reducing lesion formation on MRI.
What are the side effects of ozanimod?
- Commonly reported: Headaches, backpain, dizziness.
The main effect of ozanimod is "lymphopenia", or reduction in the number of lymphocytes. Since these cells are incorrectly attacking the brain and spinal cord in patients with MS, the number of relapses is less; however, these cells also prevent infections in our body, so patients on ozanimod can have higher chance of infection.
- These may be urinary tract infections, respiratory infections, or viral infections including varicella zoster, which causes shingles.
- Live vaccines, including the vaccination against varicella zoster, is recommended 4 to 6 weeks prior to starting ozanimod in those who are not immune against the virus. Live vaccinations are to be avoided while taking ozanimod.
- Rare opportunistic infections, including Cryptococcus and progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML), have been reported in patients treated with other S1P receptor modulators, and can be fatal. Your doctor will assess for these infections and stop ozanimod if they are suspected.
- If you have active infection, ozanimod is not recommended.
Blood counts and liver injury. To monitor for lymphopenia, and liver injury, bloodwork is checked before starting as well as every 6 months while on ozanimod, and again 6 months after the last dose.
Heart rhythm abnormalities. There are S1P receptors on the heart; therefore, there is a risk of "bradyarrhythmia", or slowing of the heart rhythm, with ozanimod. An electrocardiogram must be performed prior to ozanimod and if heart rhythm abnormalities are found, advice from a cardiologist may be required before starting ozanimod.
Hypertension, drug, and food interactions. There is a risk of "hypertension", or increased blood pressure, with ozanimod.
- This risk is increased if patients are taking certain medications, namely the monoamine oxidase type B (MAO-B) inhibitors, or consuming foods with high amounts of tyramine(such as aged cheeses, red wines, cured or processed meats, or fermented or pickled foods). It is recommended to work with your doctor and nutritionist to ensure you do not exceed 150 mg of tyramine daily in your diet.
- Hypertension can also result in swelling of the brain, resulting in a condition called “posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome” (PRES) and cause visual changes, headaches, or confusion. If you experience these symptoms on ozanimod, contact your doctor.
Breathing issues. Certain patients on ozanimod can develop breathing problems, and you should inform your doctor if you feel shortness of breath while taking this medication. If you have a history of obstructive sleep apnea, you must have it treated prior to taking ozanimod.
Macular edema. Patients taking ozanimod have an increased risk of developing macular edema. An ophthalmologist, a medical doctor with specialization in eye diseases, will assess your eyes for macular edema prior to starting ozanimod as well as after initiation and at yearly intervals after, or if there are any visual changes, including appearance of wavy distortions in the vision of one eye. Patients with history of uveitis or diabetes mellitus have a higher risk of developing macular edema and should be monitored more regularly.
Lymphocytes also are involved in monitoring the body for cancer, so patients taking ozanimod may have an increased risk of cancer.
- The randomized controlled trials of ozanimod versus interferon beta-1a reported 8 cases of cancer in ozanimod treated patients (testicular seminoma, breast cancer and basal cell carcinoma), compared to two patients in the interferon group. An increased risk of cutaneous malignancies has been reported with another S1P receptor modulator.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Based on animal studies, ZEPOSIA may cause fetal harm.
- For this reason, women of childbearing potential should use effective contraception to avoid pregnancy during treatment and for 3 months after stopping ozanimod
Breastfeeding. There is no evidence on the presence of ozanimod in human breast milk, nor evidence of harm to infants who are fed breastmilk of mothers taking ozanimod, however in animal studies higher levels of ozanimod were found in the breast milk of rats than in the plasma. The risk of continuing ozanimod, and continuing breast-feeding, is based on an individual circumstance.
Rebound disease activity. Patients who discontinue S1P receptor modulators, including ozanimod, fingolimod, or siponimod, are at risk for recurrence of MS activity in the form of new clinical relapses or new lesion formation on MRI. This is thought to occur when the medication wears off and lymphocytes begin to recirculate through the body after being trapped in the lymph nodes. This may occur anywhere from 1 to 4 months after stopping medication. Therefore, a plan should be in place to switch medications and monitor closely if these medications are to be stopped. Inform your doctor if you wish to discontinue these medications.
Contraindications: Ozanimod is not recommended in patients with the following:
- Myocardial infarction, unstable angina, stroke, transient ischemic attack (TIA), decompensated heart failure requiring hospitalization, or Class III or IV heart failure in the prior 6 months
- Have the presence of Mobitz type II second-degree or third degree atrioventricular (AV) block, sick sinus syndrome, or sinoatrial block, unless the patient has a functioning pacemaker
- Have severe untreated sleep apnea
- Are taking a monoamine oxidase type B (MAO-B) Inhibitors
How effective is ozanimod?
- Ozanimod is considered one of the "higher efficacy" medications, meaning that ozanimod reduces the number of relapses, new MRI lesions, and potentially disability progression, more so than many other treatments for MS. This leads to higher risk of adverse events, as outlined above.
- Trial 1: SUNBEAM (Comi, Lancet Neurol, 2019)
- This clinical trial compared 447 patients randomized to receive ozanimod 1.0mg with 448 patients who received interferon beta-1a
- Trial 2: RADIANCE (Cohen, Lancet Neurol, 2019)
- This clinical trial compared 433 patients randomized to receive ozanimod 1.0mg with 441 patients who received interferon beta-1a
- Relapse rates. Patients who received ozanimod had between 38-48% fewer relapses than patients who received interferon injectable medication in two 1-year trials. Between 76% and 78% of patients who received ozanimod remained relapse free during follow-up, compared to 64-66% of the patients who received interferon.
- MRI lesions. There were between 42-48% fewer new or enlarging lesions on MRI in patients who received ozanimod compared with interferon.
- Disability worsening. During the trial periods, a similar proportion of patients had worsening of their disability on either ozanimod or interferon
Both of these studies also investigated 0.5mg dosing of ozanimod, and found that 1.0mg is more effective, hence there is one currently approved dose.
For more information please see the following websites and references:
- FDA label:
- Zeposia® patient website:
References:
- Comi et al. Safety and efficacy of ozanimod versus interferon beta-1a in relapsing multiple sclerosis (SUNBEAM): a multicentre, randomised, minimum 12-month, phase 3 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2019 Nov;18(11):1009-1020. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30239-X.
- Cohen et al. Safety and efficacy of ozanimod versus interferon beta-1a in relapsing multiple sclerosis (RADIANCE): a multicentre, randomised, 24-month, phase 3 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2019 Nov;18(11):1021-1033. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30238-8.
Diroximel fumarate (Vumerity®)
Brand name: Vumerity®
Chemical name: Diroximel fumarate
Generic available: No
Dosing formulation:
Oral medication available in 231mg capsule taken twice daily by mouth. Capsules can be stored at room temperature between 68°F and 77°F
What it is:
Diroximel fumarate (Vumerity®) is a twice a day oral capsule approved by the FDA on 10/29/2019 to treat relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS). This includes clinically isolated syndrome, relapsing-remitting disease, and active secondary progressive disease in adults.
What it does:
Diroximel fumarate (Vumerity®) is similar to another disease modifying therapy: Dimethyl Fumarate (Tecfidera). But Vumerity® has a distinct chemical structure that has been shown to be better tolerated, with fewer reported gastrointestinal side effects than Tecfidera. Once in the body, Vumerity® rapidly converts to the same active ingredient as Tecfidera, which is called monomethyl fumarate (MMF). Because of that, it was not necessary for Vumerity® to undergo extensive clinical trials to demonstrate benefits for relapsing MS as its effect was considered to be similar to Tecfidera. Although their exact mechanism of action is not known, Vumerity® and Tecfidera are thought to modulate the immune response to be less inflammatory and may have antioxidant properties that could be protective against damage to the brain and spinal cord.
How effective is Vumerity/potential benefits:
In a five-week, Phase III study the gastrointestinal side effects and tolerability of Vumerity® and Tecfidera were compared. Diroximel fumarate (Vumerity®) was better tolerated and had significantly fewer reported gastrointestinal symptoms compared to Tecfidera. The most common adverse events for both treatment groups were flushing, diarrhea and nausea. Rates of these events were significantly lower for the Vumerity® group, and fewer people on Vumerity® dropped out of the study due to side effects. The approval of Vumerity® is based largely on the FDA’s findings of safety and efficacy for Tecfidera. Twice-daily Tecfidera was shown in clinical trials to significantly reduce relapses and disease activity on MRIs, and in one trial it reduced progression of disability. The Tecfidera approval was based on results of two large-scale phase III studies, called DEFINE and CONFIRM, which were conducted in people with relapsing-remitting MS. The results were published in 2012.
Dosing instructions:
- Prior to starting Vumerity® your healthcare provider should do blood tests to check your liver function and to check your white blood cell count. You should have blood tests after 6 months of treatment and every 6 to 12 months after that to check your white blood cells and if clinically necessary to check your liver function.
- The Vumerity® capsules must be swallowed whole and intact, should not be crushed or chewed and the capsule contents should not be sprinkled on food.
- Do not drink alcohol at the time you take a Vumerity® dose
- If taken with food, a high-fat, high-calorie meal/snack should be avoided (the meal/snack should contain no more than 700 calories and no more than 30 g fat)
Dosing schedule:
You will start with taking one 231mg capsule twice per day, one in the morning and one in the evening and after day 7, you will switch to maintenance dose of two capsules twice per day.
| Starting dose day 1-7 | Maintenance dose after day 7 |
|---|---|
| One 231mg capsules, in the morning and in the evening | Two 231mg (462mg) capsules, in the morning and in the evening |
Do not take Vumerity if you:
- Have had an allergic reaction (such as welts, hives, swelling of the face, lips, mouth or tongue, or difficulty breathing) to diroximel fumarate, dimethyl fumarate, or any of the ingredients in Vumerity®
- Are taking dimethyl fumarate (Tecfidera)
Before taking and while you take Vumerity®, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- Have liver problems
- Have kidney problems
- Have or have had low white blood cell counts or an infection
- Are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if Vumerity® will harm your unborn baby
- Are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if Vumerity® passes into your breast milk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby while using Vumerity®.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
What are the possible side effects of Vumerity®?
- The most common side effects of this medication include:
- Flushing, redness, itching, or rash
- Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomach pain, or indigestion
- Flushing and stomach problems are the most common reactions, especially at the start of therapy, and may decrease over time. Taking Vumerity® with food (avoid high-fat, high-calorie meal or snack) may help reduce flushing. Call your healthcare provider if you have any of these symptoms and they bother you or do not go away. Ask your healthcare provider if taking aspirin before taking Vumerity® may reduce flushing.
- Vumerity® may cause serious side effects including:
- Allergic reaction(such as welts, hives, swelling of the face, lips, mouth or tongue, or difficulty breathing). Stop taking Vumerity® and get emergency medical help right away if you get any of these symptoms
- PML (progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy)a rare brain infection that usually leads to death or severe disability over a period of weeks or months. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get any of these symptoms of PML:
- Weakness on one side of the body that gets worse
- Clumsiness in your arms or legs
- Vision problems
- Changes in thinking and memory
- Confusion
- Personality changes
- Herpes zoster infections (shingles), including central nervous system infections
- Other serious infections
- Decreases in your white blood cell count. Your healthcare provider will monitor your blood counts in a regular basis.
- Liver problems. Your healthcare provider will check your liver function before staring the treatment and monitor that as needed. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get any of these symptoms of a liver problem during treatment
- Severe tiredness
- Loss of appetite
- Pain on the right side of your stomach
- Have dark or brown (tea color) urine
- Yellowing of your skin or the white part of your eyes
Use in specific populations
- Children: It is not known if Vumerity® is safe or effective in children
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: It is not known if Vumerity® will harm your unborn baby. It is not known if Vumerity® passes into your breast milk. You should always talk to your healthcare provider before taking Vumerity® if you are pregnant, interested in becoming pregnant, breastfeeding or planning to breastfeed.
- Kidney issue/renal impairment: No dosage adjustment is necessary in patients with mild kidney issues. Use of Vumerity® is not recommended in patients with moderate or severe renal impairment
COVID19 related information:
- The evidence available suggests that people with MS taking dimethyl fumarate (Tecfidera) or diroximel fumarate (Vumerity®) do not have an increased risk of more severe COVID-19 symptoms.
- For vaccination related information please refer to our COVID19 information website:
- And also National MS Society website:
For more information on Vumerity®, please see the following:
- National MS Society:
- FDA label:
- Vumerity® patient website:
References:
- VUMERITY Prescribing Information, Biogen, Cambridge, MA.
- Naismith RT, et al. CNS Drugs. 2020;34(2):185-196.
Ofatumumab (Kesimpta®)
Brand name: Kesimpta®
Chemical name: Ofatumumab
Generic available: No
Dosing formulation:
This medication is taken by injection, comes in prefilled syringe or pen, can be self-administered monthly via subcutaneous injection at one's home via the Sensoready® autoinjector pen. Pens must be refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F).
What it is:
Ofatumumab (Kesimpta®) is the first self-administered anti B-cell therapy for MS, was approved by the FDA on August 20, 2020 to treat relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS). This includes clinically isolated syndrome, relapsing-remitting disease, and active secondary progressive disease in adults.
Background information:
According to Novartis, ofatumumab was first approved by the FDA in 2009 for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), given in a high-dose intravenous infusion. Knowing that B-cells are involved with the development of autoimmune diseases, ofatumumab was then studied as a potential treatment for relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (RMS). The clinical development of ofatumumab for RMS and its novel administration required 10 years to complete and more than 2,300 participants to take part in rigorous, international clinical trials.
What it does:
In the same class as ocrelizumab (Ocrevus®), Kesimpta is a therapy that depletes specific immune B cells. B cells are among immune cells that have been implicated in causing nervous system damage in MS. Kesimpta is a monoclonal antibody that binds to a docking site (CD20) a protein found on the surface of specific immune B cells (lymphocytes) and depletes them.
B-cell therapies such as ocrelizumab were previously only available via infusions every couple of months at a hospital or infusion center; however, Kesimpta is the first self-administered B-cell therapy for MS. It is given monthly via subcutaneous injection at one’s home, providing individuals with MS a new and convenient option for treating their MS.
How effective is Kesimpta/potential benefits:
The approval of Kesimpta is based on results from two identical Phase 3 studies (ASCLEPIOS I and II), in which Kesimpta demonstrated superiority over Aubagio® (oral teriflunomide) in significantly reducing annual relapses, reducing disability worsening at three months, and reducing disease activity on MRI.
These trials examined the efficacy and safety of Kesimpta relative to Aubagio in more than 1,800 people aged 18-55 years with RMS participated in which participants were randomly assigned to receive Kesimpta self-injected once a month, or daily oral Aubagio for up to 30 months. As a control, the groups also received placebo versions of Kesimpta or Aubagio.
RMS patients on ofatumumab (Kesimpta) had a reduction in annualized relapse rate by 50.5% (0.11 vs. 0.22) and 58.5% (0.10 vs. 0.25) compared to Aubagio®* (teriflunomide) (both studies p<0.001) in ASCLEPIOS I and II studies, respectively. Ofatumumab compared to Aubagio® showed highly significant suppression of gadolinium (Gd) T1 lesions by 98% (0.01 vs 0.45) and 94% (0.03 vs 0.51) and fewer T2 lesions by 82% (0.72 vs 4) and 85% (0.64 vs 4.15) in ASCLEPIOS I and II studies respectively (both studies p<0.001). This demonstrated a profound suppression of new inflammatory activity in patients treated with Kesimpta compared to Aubagio. The studies also showed a relative risk reduction of 34.4% in 3-month confirmed disability progression (p=0.002) and 32.5% in 6-month confirmed disability progression (p=0.012) in ofatumumab compared to Aubagio.
There was also an open-label Phase II trial, APLIOS study, conducted to assessed if different delivery methods (prefilled syringe vs Sensoready® autoinjector pen) would lead to similar blood concentrations of ofatumumab, and produce the same effects in the body. The study showed similar systemic exposure to ofatumumab across different injection sites (abdomen or thigh) and bioequivalence was demonstrated between the prefilled syringe and Autoinjector pen. All the studies and results detailed above has shown Kesimpta to be a highly effective B-cell therapy that can be easily self-administered at home
Before you take Kesimpta, tell your healthcare provider (HCP) about all your medical conditions, including if you:
- Have or think you have an infection.
- Have ever taken, currently take, or plan to take medicines that affect your immune system.
- Have had a recent vaccination or are scheduled to receive any vaccinations.
- Are pregnant, think that you might be pregnant, or plan to become pregnant.
- Are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed.
Tell your HCP about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Do not take Kesimpta if you:
Have active hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection.
Assessments prior to first dose of Kesimpta:
- Hepatitis B Virus Screening
- Hepatitis B virus (HBV) screening should be performed in all patients before initiation of treatment with Kesimpta. At a minimum, screening should include Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) and Hepatitis B Core Antibody (HBcAb) testing which is done with blood work. These can be complemented with other appropriate markers as per local guidelines. For patients who are negative for HBsAg and positive for HB core antibody [HBcAb+] or are carriers of HBV [HBsAg+], liver disease experts will be consulted before starting and during treatment with Kesimpta.
- Serum Immunoglobulins
- Quantitative serum immunoglobulins levels will be checked also with blood work. For patients with low serum immunoglobulins, further more extensive immunological/hematological tests and reviews will be considered before initiating treatment with Kesimpta.
- Vaccinations
- Vaccination with live-attenuated or live vaccines is not recommended during treatment and after discontinuation of Kesimpta until B-cell repletion. So if live or live-attenuated vaccines are necessary according to immunization guidelines, they must be administered at least 4 weeks before initiating Kesimpta, and inactivated vaccines can be administered at least 2 weeks before initiating Kesimpta.
Assessment during Kesimpta treatment:
- Individuals prescribed Kesimpta are required to have blood tests to be screened for the presence of Hepatitis B virus (HBV), and to be screened for serum levels of immunoglobulins before, during and after discontinuing treatment until B cells return in routine intervals as per clinical decision.
Dosing instructions:
- See the detailed Instructions for Use that comes with Kesimpta for information about how to prepare and inject a dose of Kesimpta and how to properly throw away (dispose of) used Kesimpta Sensoready pens or prefilled syringes.
- Use Kesimpta exactly as your HCP tells you to use it.
- Your HCP will show you how to prepare and inject Kesimpta the right way before you use it for the first time.
- Do not inject into areas where the skin is tender, bruised, red, scaly or hard. Avoid areas with moles, scars, or stretch marks.
Dosing schedule
- Available doses:
- 20mg/0.4mL single-dose prefilled Sensoready pen
- 20mg/0.4mL single-dose prefilled syringe
When starting Kesimpta, individuals will take injections each week for 3 weeks, skip one week, and thereafter will take Kesimpta monthly. Take on the same day of the week, like Mondays for example.
| Starting dose weeks 0 to 3 | Maintenance dose from week 4 |
|---|---|
| Weekly injection: week 0,1,2 but skip week 3 | Monthly injections |
What are the possible side effects of Kesimpta?
The most common side effects of this medication (incidence greater than 10%) include:
- Upper respiratory tract infection, with symptoms such as sore throat and runny nose
- Headache
- Local injection side reaction
- Injection-related reactions: can happen within 24 hours following the first injection and with later injections. Talk with your HCP if you have any of these signs and symptoms:
- Redness of the skin, swelling, itching, or pain at or near the injection site
- Fever, headache, pain in the muscles, chills, and tiredness
Kesimpta may cause serious side effects including:
- Low immunoglobulins: kesimpta may cause a decrease in some types of antibodies. Your HCP will do blood tests to check your blood immunoglobulin levels in routine intervals.
- Infections: Serious infections can happen during treatment with Kesimpta. If you have an active infection, your doctor should delay your treatment with Kesimpta until your infection is gone. Kesimpta taken before or after other medicines that weaken the immune system may increase your risk of getting infections. Tell your HCP right away if you have any infections or get any symptoms including painful and frequent urination, nasal congestion, runny nose, sore throat, fever, chills, cough, or body aches.
- HBV reactivation. There were no reports of HBV reactivation in patients with MS treated with Kesimpta. However, HBV reactivation, in some cases resulting in fulminant hepatitis, hepatic failure, and death, has occurred in patients being treated with ofatumumab for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) (at higher intravenous doses than the recommended dose in MS but for a shorter duration of treatment) and in patients treated with other anti-CD20 antibodies.
- If you have ever had HBV infection, it may become active again during or after treatment with Kesimpta (reactivation). If this happens, it may cause serious liver problems including liver failure or other more severe complications. Before starting Kesimpta, your HCP will do a blood test to check for HBV. They will also continue to monitor you during and after treatment with Kesimpta. Tell your HCP right away if you get worsening tiredness or yellowing of your skin or the white part of your eyes.
- Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML). PML may happen with Kesimpta. PML is a rare, serious brain infection caused by a virus that may get worse over days or weeks. PML can result in death or severe disability. Tell your HCP right away if you have any new or worsening neurologic signs or symptoms. These may include weakness on one side of your body, loss of coordination in arms and legs, vision problems, changes in thinking and memory, which may lead to confusion and personality changes.
Use in specific populations
- Children: It is not known if Kesimpta is safe or effective in children.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: There are no adequate data on the developmental risk associated with the use of Kesimpta in pregnant women. Ofatumumab may cross the placenta and cause fetal B-cell depletion based on findings from animal studies. Transient peripheral B-cell depletion and lymphocytopenia have been reported in infants born to mothers exposed to other anti-CD20 B-cell depleting antibodies during pregnancy. Therefore, due to possible risk for fetal harm, females who can become pregnant should use birth control (contraception) during treatment with Kesimpta and for 6 months after last Kesimpta treatment. Talk with your HCP about what birth control method is right for you during this time. It is not known if Kesimpta passes into your breast milk. You should always talk to your healthcare provider before taking Kesimpta if you are breastfeeding or planning to breastfeed.
COVID19 related information:
- There is some evidence that therapies that target CD20 – including Kesimpta (ofatumumab), Ocrevus (ocrelizumab), and Rituxan (rituximab)– may be linked to an increased chance of being admitted to hospital or requiring intensive care treatment due to COVID-19. Before starting on any new disease-modifying therapy, people with MS should discuss with their healthcare professional which therapy is the best choice for their individual disease course and disease activity in light of COVID-19 risk in their region.
- For vaccination related information please refer to our COVID19 information website:
- And also National MS Society website:
For more information on Kesimpta, please see the following:
- National MS Society:
- Kesimpta patient website:
- https://www. Kesimpta.com/
- Kesimpta drug information website:
- FDA label:
References:
- Kesimpta Prescribing Information. East Hanover, NJ: Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp; August 2020.
- Hauser S, Bar-Or A, Cohen J, et al. Ofatumumab versus teriflunomide in relapsing multiple sclerosis: analysis of no evidence of disease activity (NEDA-3) from ASCLEPIOS I and II trials. Eur J Neurol. 2020;27(S1).
- Bar-Or A, Fox E, Goodyear A, et al. Onset of B-cell depletion with subcutaneous administration of ofatumumab in relapsing multiple sclerosis: results from the APLIOS bioequivalence study. Poster presentation at: ACTRIMS; February 2020; West Palm Beach, FL.
Flu Shots
What do I need to know about the flu vaccine?
- The 2016-2017 inactivated seasonal influenza (flu) immunization is a single injection that provides immunity to three or four different flu viruses.
- The 2016-2017 inactivated seasonal flu immunization is recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) for everyone over 6 months of age.
- The seasonal flu vaccine has been studied extensively in people with MS and is considered quite safe, regardless of the disease-modifying therapy they are taking.
- A high-dose inactivated flu vaccine (Fluzone High Dose) is available for people over age 65. The high-dose vaccine has not been studied in people with MS of any age. For these reasons, we recommend that only the standard dose of the influenza vaccination (flu shots) be used for people with MS.
- Getting vaccinated before flu season begins is the most effective way to prevent flu. For these reasons, the CDC recommends that people get a flu vaccine by the end of October, if possible. However, getting vaccinated later can still be beneficial. The CDC recommends ongoing flu vaccination as long as influenza viruses are circulating, even into January or later.
- Hard Immunity – If you can't get vaccinated for some reason, make sure people in your immediate family and household are vaccinated.
Are their specific studies that show the flu vaccine is safe for MS patients?
- A study by the Vaccines in Multiple Sclerosis Study Group published in 2001 in the New England Journal of Medicine found that vaccination for tetanus, hepatitis B or influenza did not appear to increase the short-term risk of relapses (also called attacks or exacerbations) in people with MS.
- A study by the National Immunization Program of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, published in the Archives of Neurology in 2003, found that vaccination against hepatitis B, influenza, tetanus, measles, or rubella did not increase a person's risk of developing MS or optic neuritis (which is often a first symptom of MS).
If I am on a specific disease modifying therapy, will the vaccine be effective?
- A study published in Neurology in 2015, evaluated the effectiveness of the flu vaccine in fingolimod-treated patients. Researchers found that most fingolimod-treated patients with MS were able to mount immune responses with the vaccine, and the majority met criteria indicating seroprotection. However, response rates were reduced compared with placebo-treated patients. Overall, there was some decrease in vaccination-induced immune responses among the fingolimod treated patients. Despite this, we still recommend that patients on Fingolimod receive a flu vaccine. http://www.neurology.org/content/84/9/872.short
- A study, published in Neurology in 2013, investigated the effect of teriflunomideon the efficacy and safety of the influenza vaccine and found that teriflunomide-treated patients generally mounted effective immune responses to seasonal influenza vaccination. Researchers concluded that teriflunomide generally does not adversely impact the ability of MS patients to mount immune responses to influenza vaccination. http://www.neurology.org/content/81/6/552.short
- A small case-control study, published in Neurology in 2013, assessed immunocompetence in patients after alemtuzumab treatment by measuring antibody responses to several vaccines before and after treatment. Researchers concluded that serum antibodies against common viruses remained detectable after treatment, and there was retained ability to mount an immune response against new antigens after treatment with alemtuzumab. http://www.neurology.org/content/81/10/872.shortWe recommend that patients on Lemtrada (Alemtuzumab) get their flu vaccine about 6 weeks before their infusion.
- If you are taking interferon beta 1a (Avonex, Rebif), glatiramer acetate (Copaxone), or natalizumab (Tysabri), the flu vaccine is likely effective. This is based on these medications' mechanisms of action.
- There is limited data on the efficacy of the flu vaccine for dimethyl fumarate (Tecfidera) and ocrelizumab.